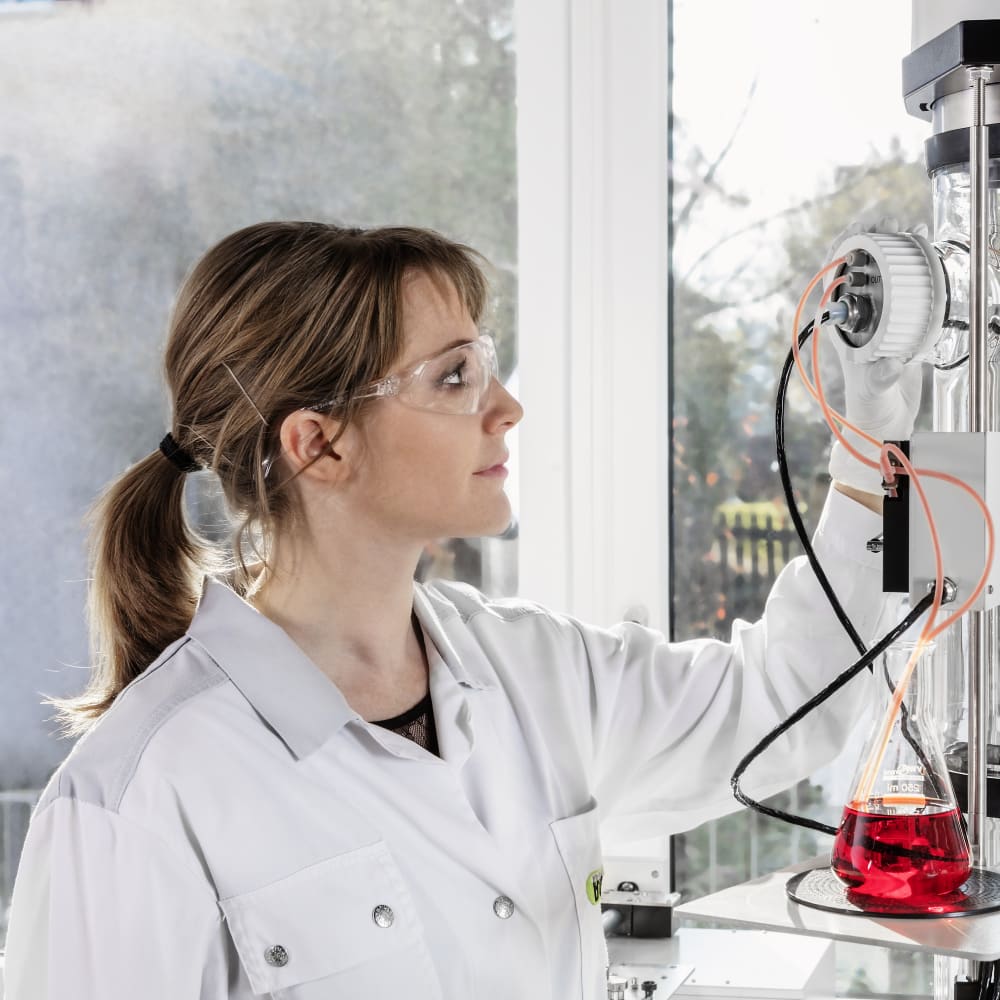
Freeze drying of beads containing yeasts
The cell viabilities of microorganisms during storage are of economic importance for probiotic dietary food and feed supplements. By combining granulation and freeze drying, dust free particles homogeneous in size and composition can be obtained. This will enable a good particle flowability, an easier dosage and a faster reconstitution of the product can be obtained. Encapsulator as a granulator to prill the yeasts suspension into liquid nitrogen and form monodispersed beads that will then be freeze dried.
Lyophilisation of fresh banana slices
Freeze drying is a gentle form of drying and may be used to preserve foods without changing their appearance or taste. The freeze drying process includes the freezing of the food sample and subsequent applying a fine vacuum to the frozen sample. Under these conditions, the water in the food will sublimate, hence, the sample dries. In food applications, freeze drying is commonly used to make instant coffee and to dry and conserve fruits, vegetables or herbs.
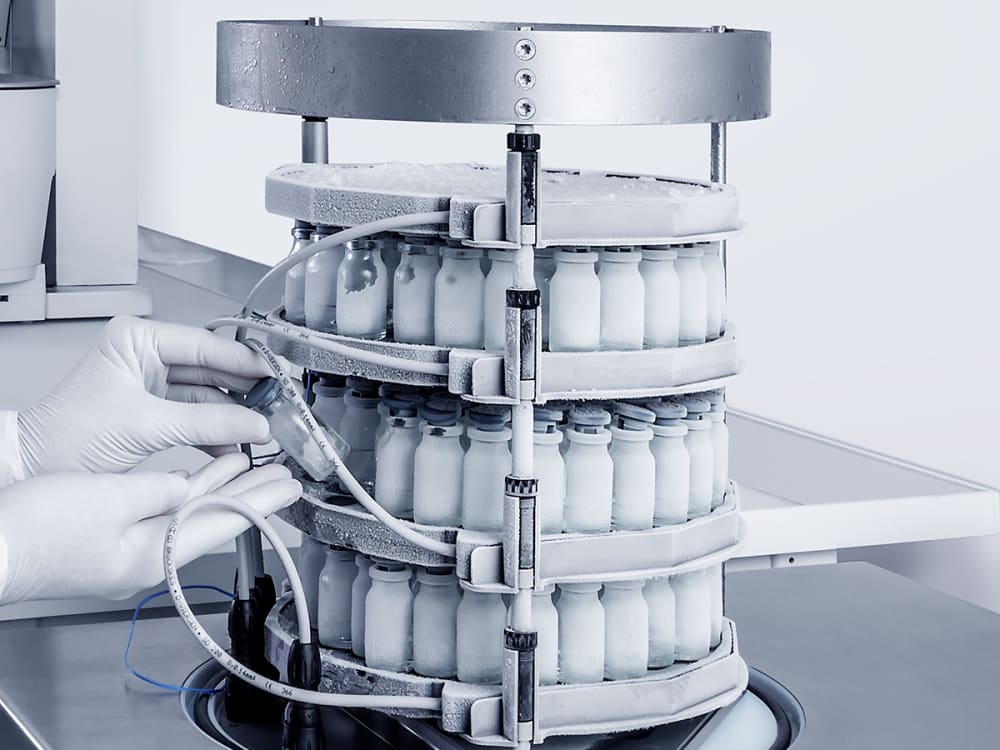
Lyophilisation of mannitol and NaCl solutions in serum vials
In this Application Note sodium chloride (NaCl) and mannitol are used for freeze drying experiments. The unambiguous crystal structure of NaCl renders this salt a model compound. In contrast, mannitol is well known to crystallize in different polymorphs and it may form hydrates. Nevertheless, mannitol is the most used bulking agent for freeze dried pharmaceutical formulations. The benefits of using mannitol are that it crystallizes during freezing, creates a beautiful cake and permits drying processes at higher product temperatures, thus with higher sublimation rates compared to purely amorphous systems.