Applications
Freeze drying of beads containing yeasts
The cell viabilities of microorganisms during storage are of economic importance for probiotic dietary food and feed supplements. By combining granulation and freeze drying, dust free particles homogeneous in size and composition can be obtained. This will enable a good particle flowability, an easier dosage and a faster reconstitution of the product can be obtained. Encapsulator as a granulator to prill the yeasts suspension into liquid nitrogen and form monodispersed beads that will then be freeze dried.
Lyophilisation of fresh banana slices
Freeze drying is a gentle form of drying and may be used to preserve foods without changing their appearance or taste. The freeze drying process includes the freezing of the food sample and subsequent applying a fine vacuum to the frozen sample. Under these conditions, the water in the food will sublimate, hence, the sample dries. In food applications, freeze drying is commonly used to make instant coffee and to dry and conserve fruits, vegetables or herbs.
Lyophilisation of mannitol and NaCl solutions in serum vials
In this Application Note sodium chloride (NaCl) and mannitol are used for freeze drying experiments. The unambiguous crystal structure of NaCl renders this salt a model compound. In contrast, mannitol is well known to crystallize in different polymorphs and it may form hydrates. Nevertheless, mannitol is the most used bulking agent for freeze dried pharmaceutical formulations. The benefits of using mannitol are that it crystallizes during freezing, creates a beautiful cake and permits drying processes at higher product temperatures, thus with higher sublimation rates compared to purely amorphous systems.
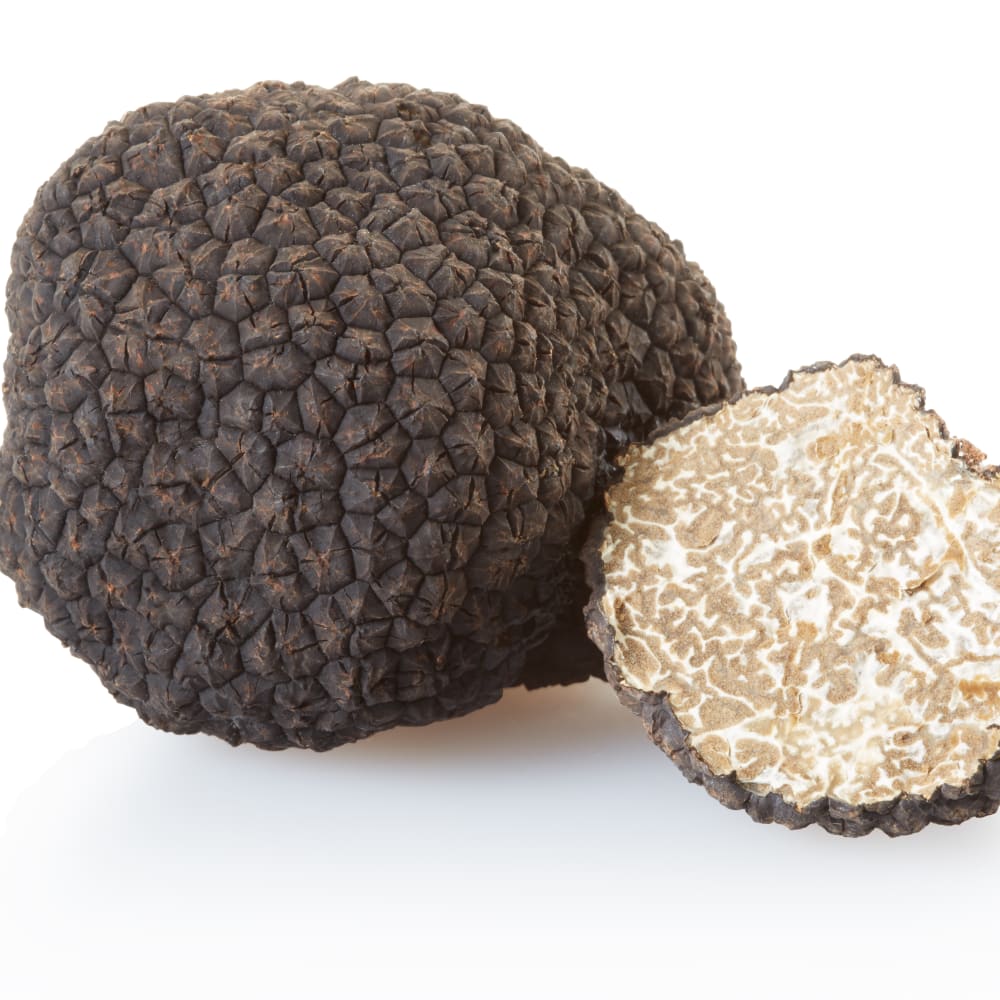
Lyophilisation of truffles
Truffles are products with limited shelf life and their sensory properties are rapidly lost. Hence, the expensive fungi become less valuable within a few days. Losses of volatile compounds, oxidation and enzymatic reactions are a considerable problem during their storage. Furthermore, the aroma profile is commonly modified as a result of elevated temperature processes or enzymatic reactions. Freeze drying the fungi avoids loss and degradation of volatile compounds due to the low temperatures applied during drying. The aromatic profile of truffles are maintained. Freeze dried truffles can either be rehydrated or directly used in dry form.
Cosmetics Lab Magazine Vol 2
In "COSMETICS LAB" Issue 2, gain useful information on how to turn natural raw material into active compounds. Benefit from useful information on techniques used in all steps of cosmetics development. Learn how to extract and screen for active ingredients and how to use chromatography to purify raw material. Plus fun facts, horoscopes, quizzes and an exclusive interview on the topic of fighting misinformation in the cosmetics industry.

Cosmetics Lab Magazine Vol 3
In "COSMETICS LAB" Issue 3, find everything you need to know about the making of make-up. Improve your formulation proficiency by gaining insightful information on microencapsulation and spray drying. Plus read cosmetics formulation tips, recipes, quizzes, horscopes and an exlcusive interview with a microencapsulation expert.

Formulation adviser for cannabis oil samples
With this free whitepaper, gain useful insights into spray drying and encapsulation, two common techniques used to formulate cannabinoids. Plus, learn about why we need cannabinoids in powder form in the first place.
Use the guide to easily achieve a sellable form of cannabinoids.
Graphene-based composites for lithium batteries by spray drying
Graphene-based composites can be used to improve the electric conductivity and cycling performance of lithium batteries (LIBs). In this whitepaper, learn more about the steps needed to obtain graphene-based composites using the spray drying technique. Benefit from an illustartion of how graphene-based composites are synthesized, learn about the function of various graphene powders in battery R&D and see process parameters for spray drying of various graphene-based material.