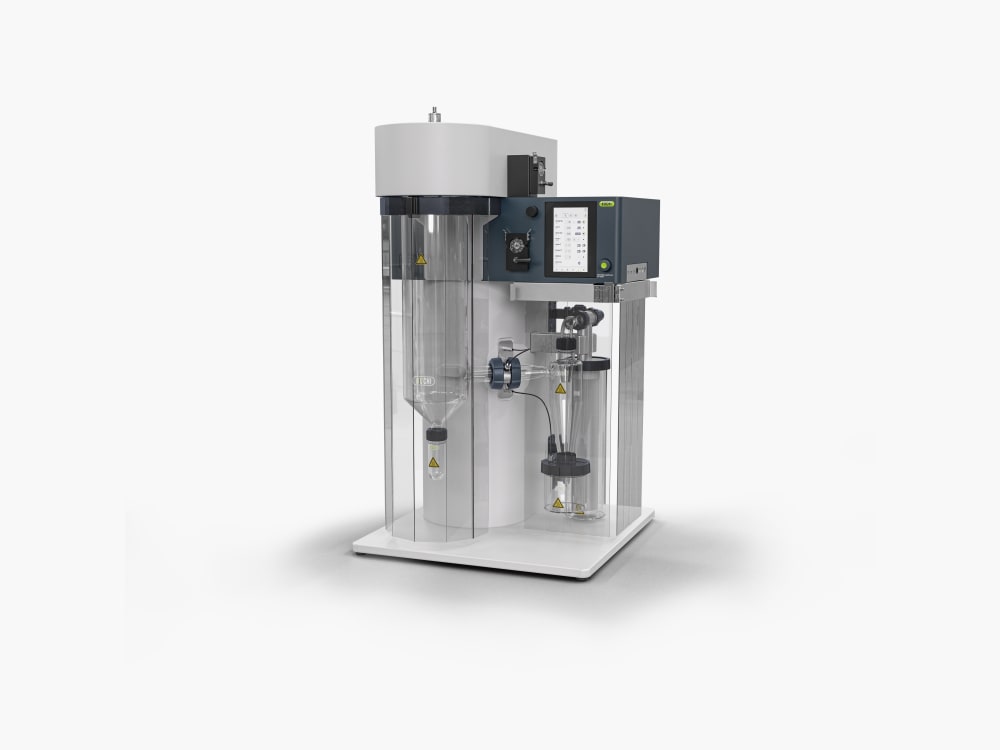
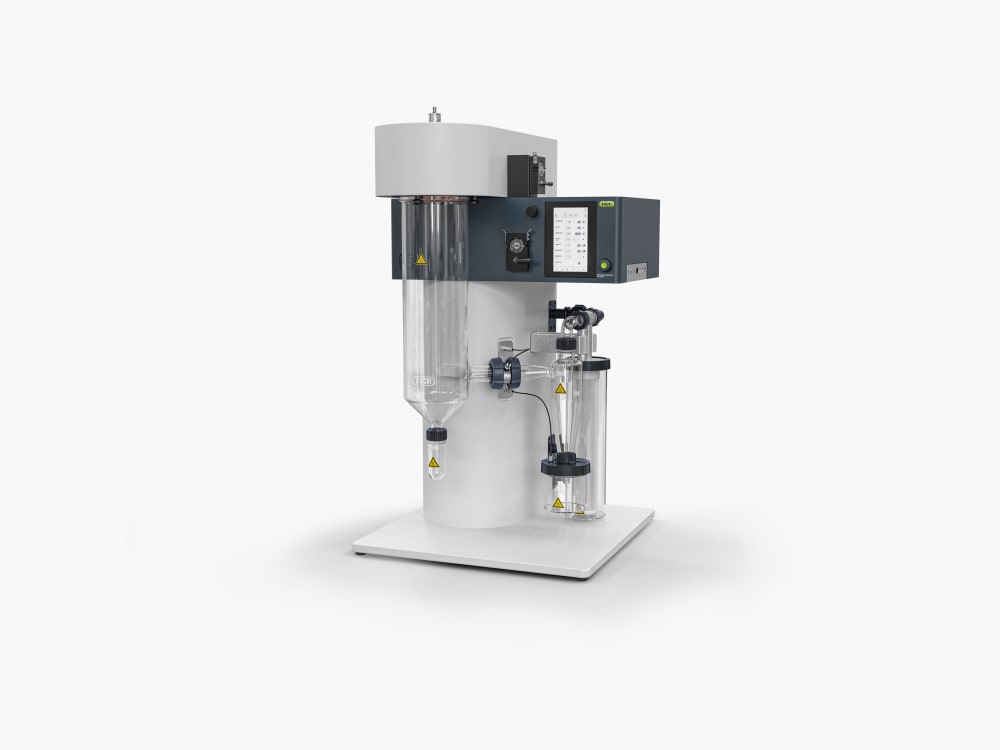
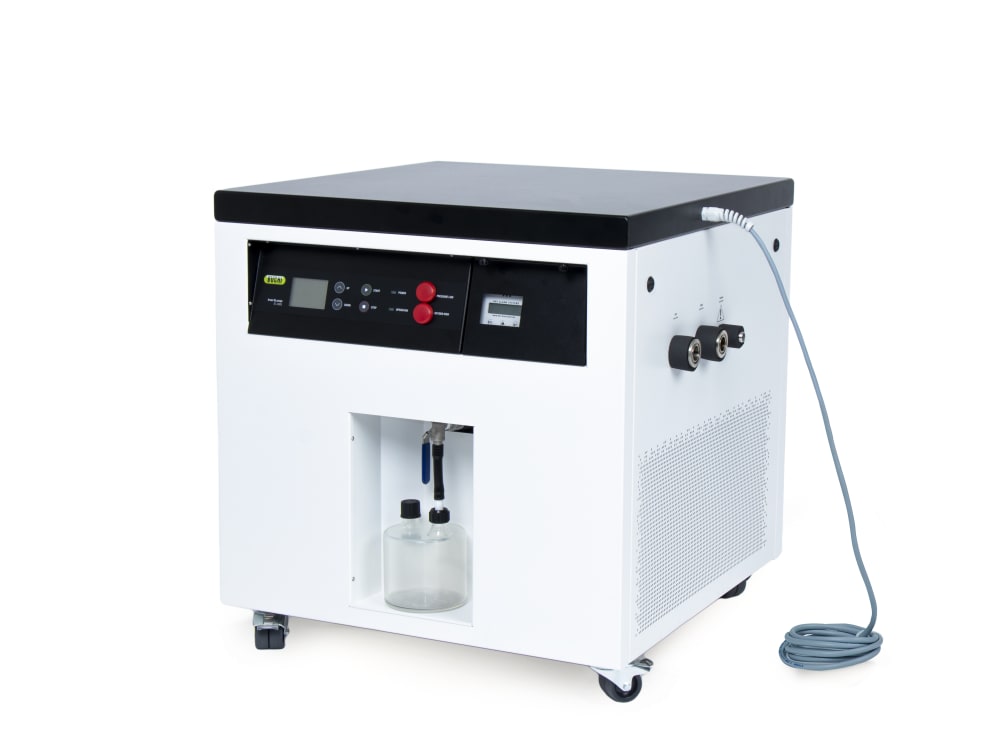
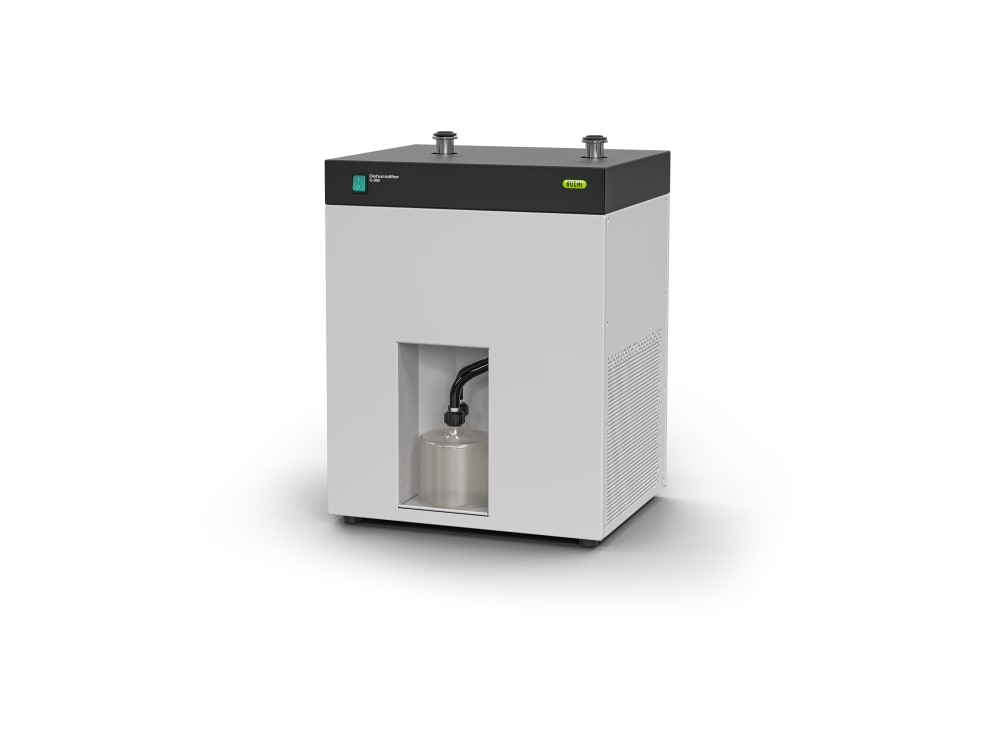
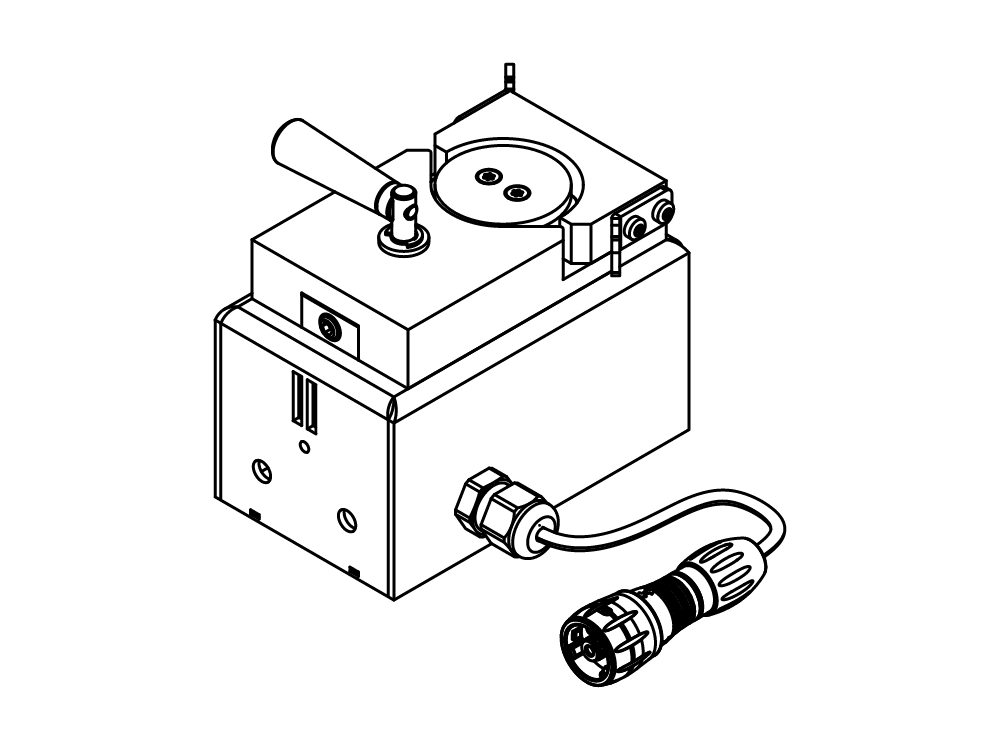
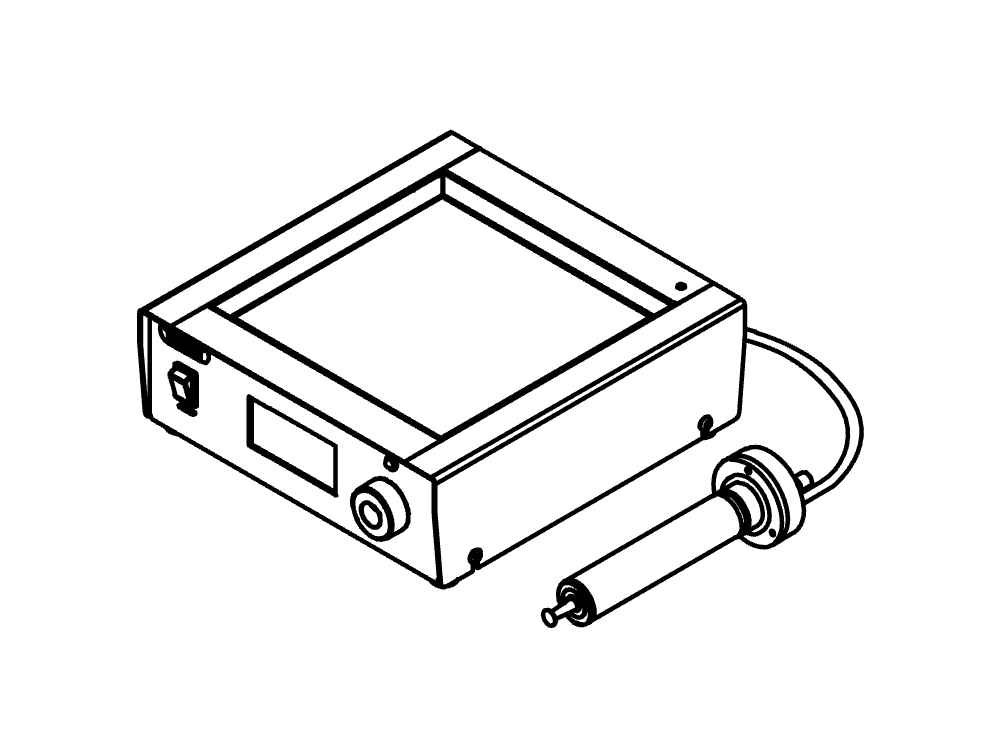
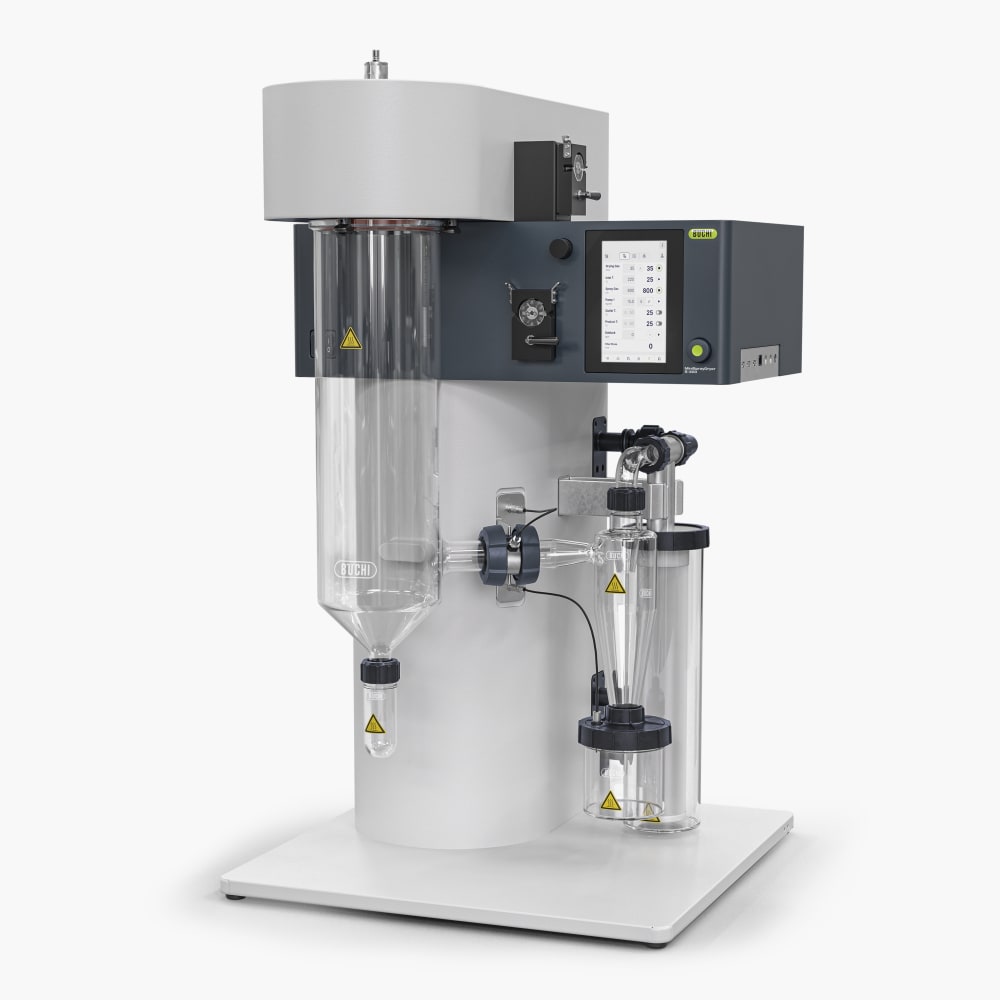
ミニスプレードライヤー S-300
次世代のラボスケールのスプレードライヤー
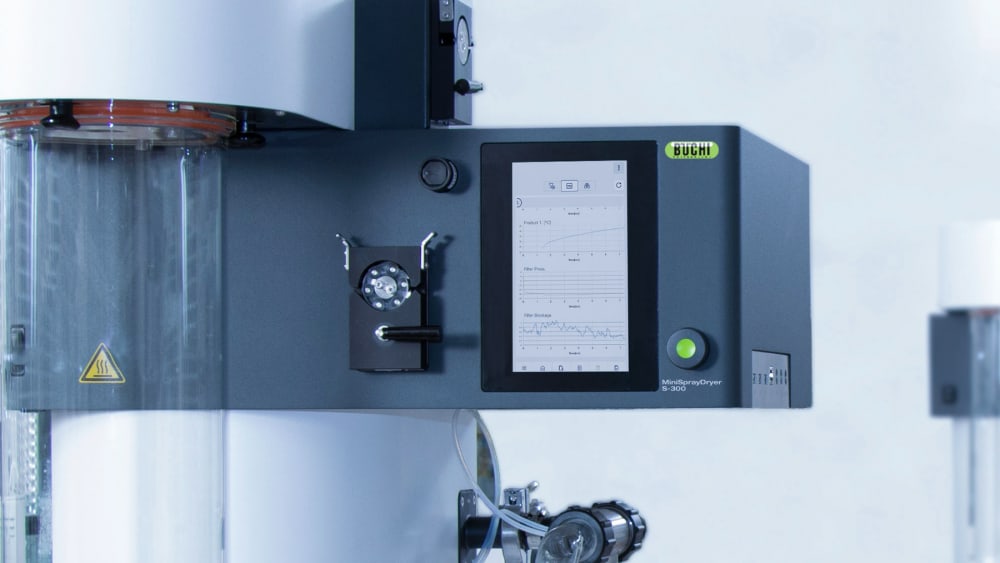
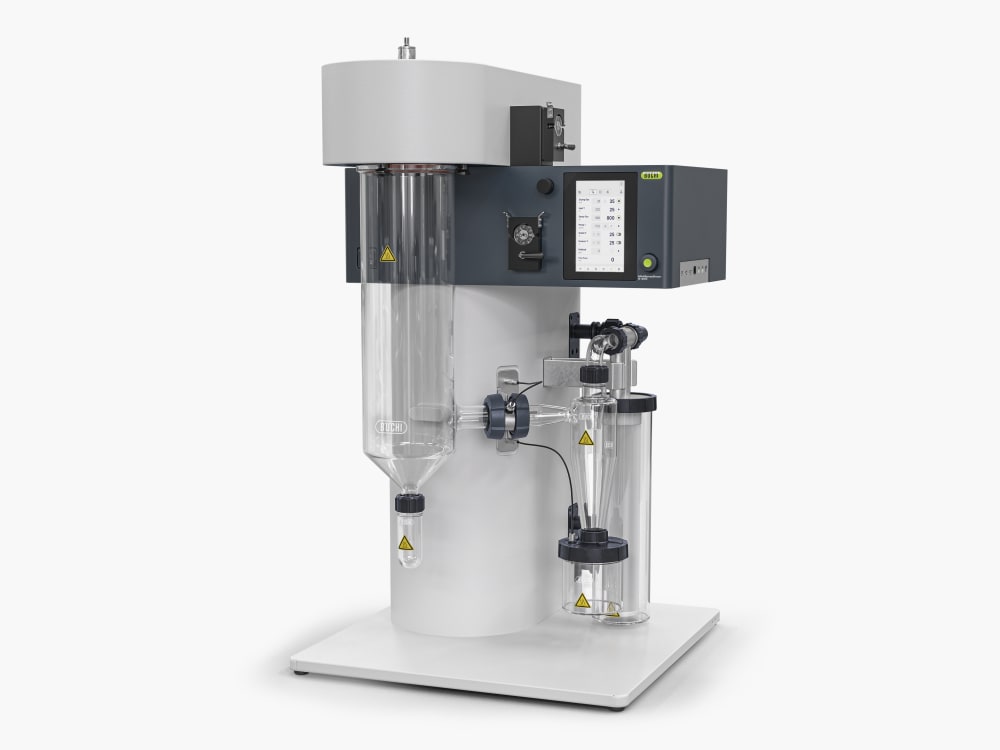
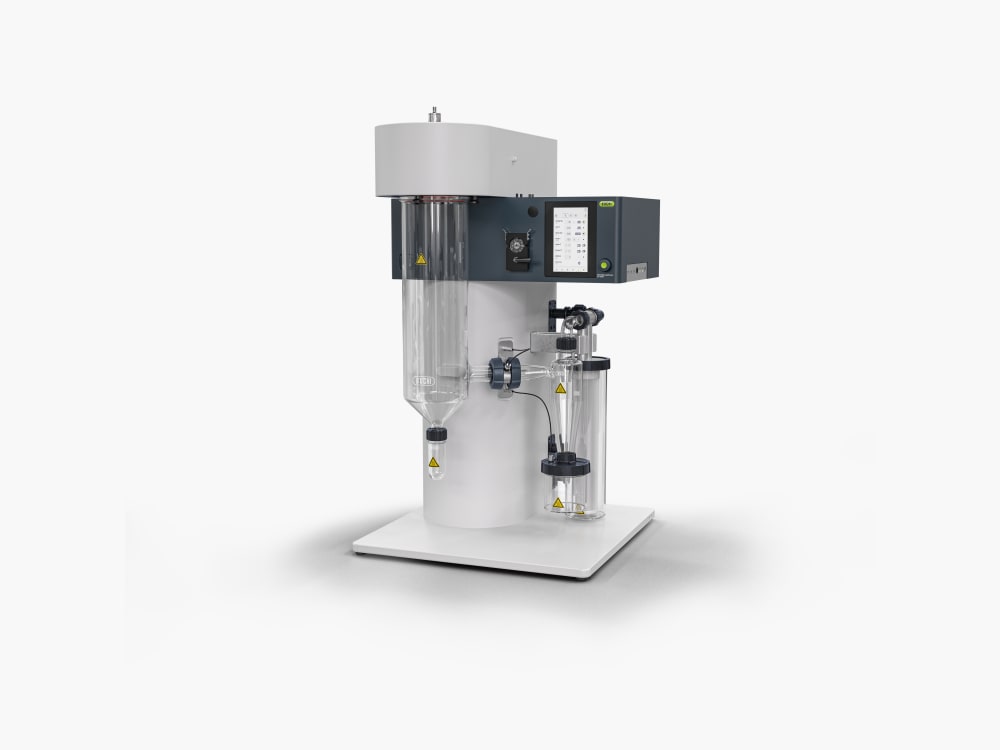
ミニスプレードライヤー S-300により、ビュッヒは40年以上にわたるグローバル市場のリーダーとしての地位を確固たるものにしました。これは卓越した製品設計と独自の装置機能を融合させ、優れたユーザーエクスペリエンスを提供する実験室用のスプレードライヤーです。

特徴
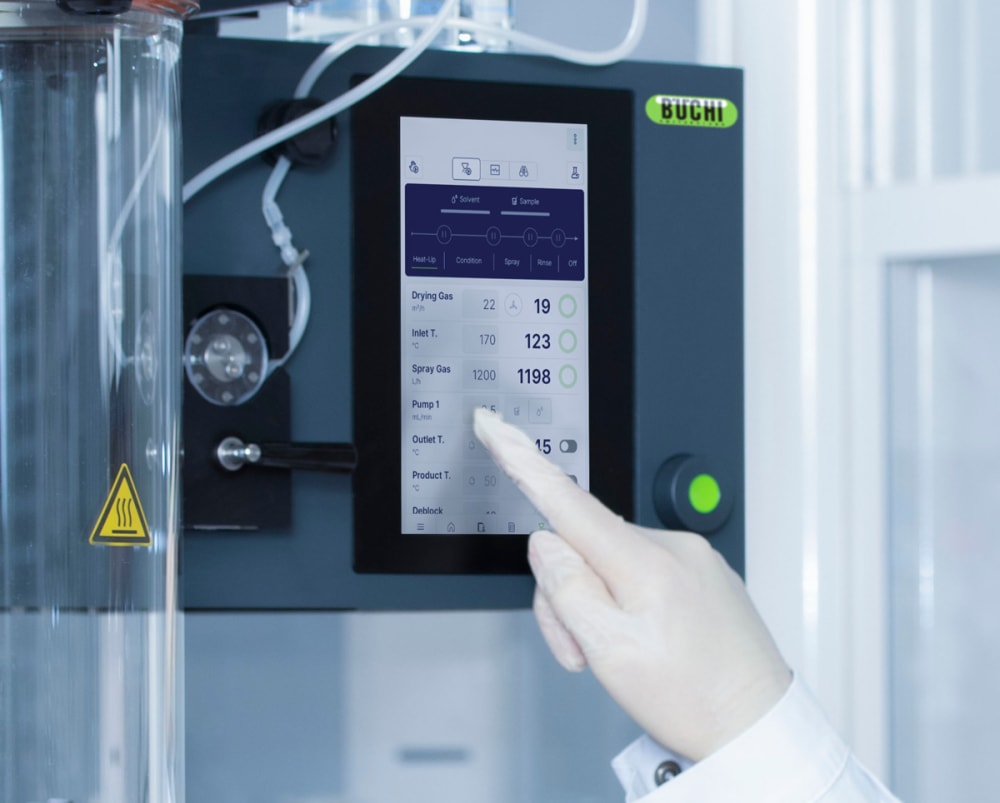
- ミニスプレードライヤー S-300は場所や時間に関係なく制御や監視が可能です。モバイル端末やパソコンのアプリから実験室に置かれたスプレードライヤーのインターフェイスにアクセスできます。リモートコントロールオプションにより柔軟な時間管理や処理変更への迅速な対応が可能になります。
- ビュッヒは、40年以上にわたるラボスケールのスプレードライの経験から膨大な応用ノウハウを蓄積してきました。公表されたビュッヒのスプレードライヤーに関する多数の文献や当社のスプレードライの応用に関するオンラインデータベースを検索して、ニーズに合ったアプリケーションを探すことができます。ミニスプレードライヤー S-300は旧モデルのスプレードライヤーの結果を再現できます。よって大切な作業を損なうことなく、迅速かつシームレスにこの新しい装置に移行することが可能です。
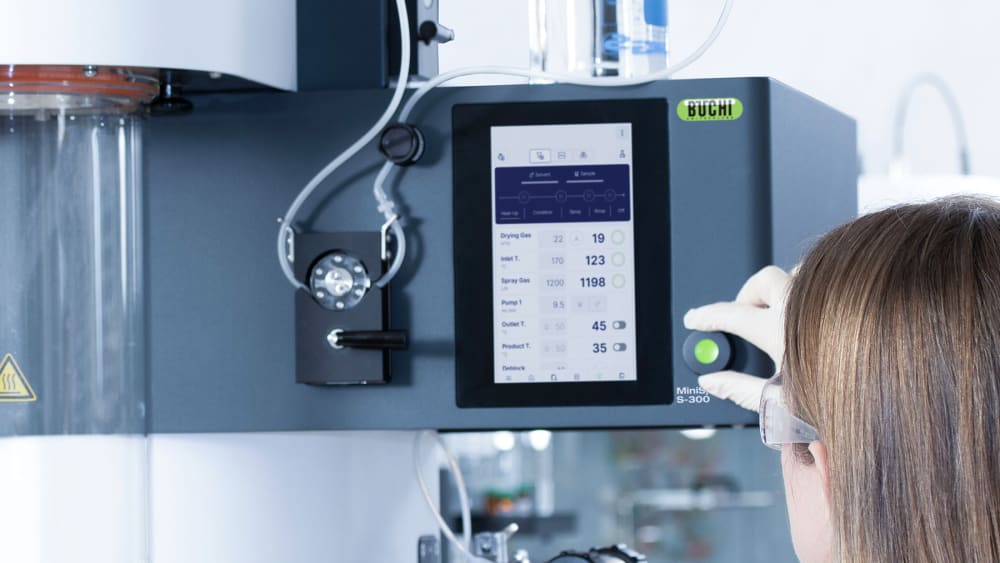
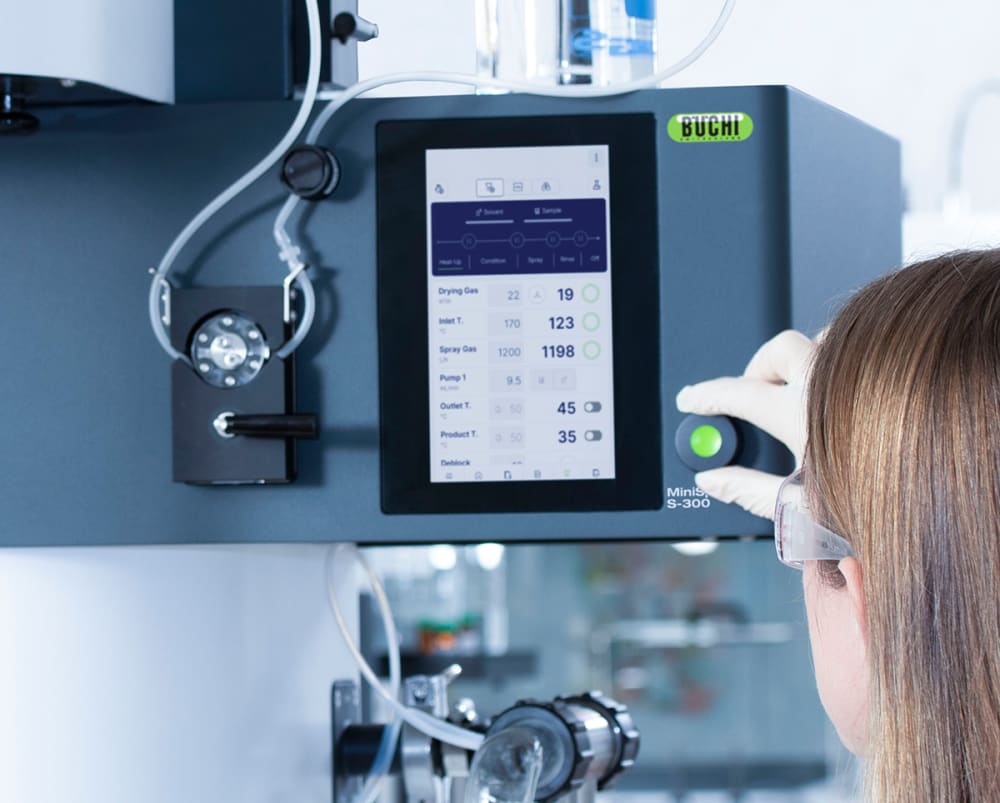
- ミニスプレードライヤー S-300アドバンスの自動モードでは、運転条件メソッドをプログラムによって自動的に実行することができます。スプレードライヤーの加熱温度や出口温度の調整、純溶媒の噴霧、試料の噴霧、純溶媒の再噴霧を行い、運転が終了したらシャットダウンします。自動モードは、特に同じ処理を繰り返し行う際の処理時間の効率を向上させます。
- 導電性コーティングを施したサイクロンにより、静電気によるサイクロン内壁への試料の付着が抑えられるため、スプレードライにおける試料のロスが低減します。
- 実際の運転条件をメソッドとして保存して繰り返し実行できるため、時間を節約し手間を省くことが可能です。また、S-300には複数のメソッドを保存して実行させる事も簡単にできるのでさらに便利です。
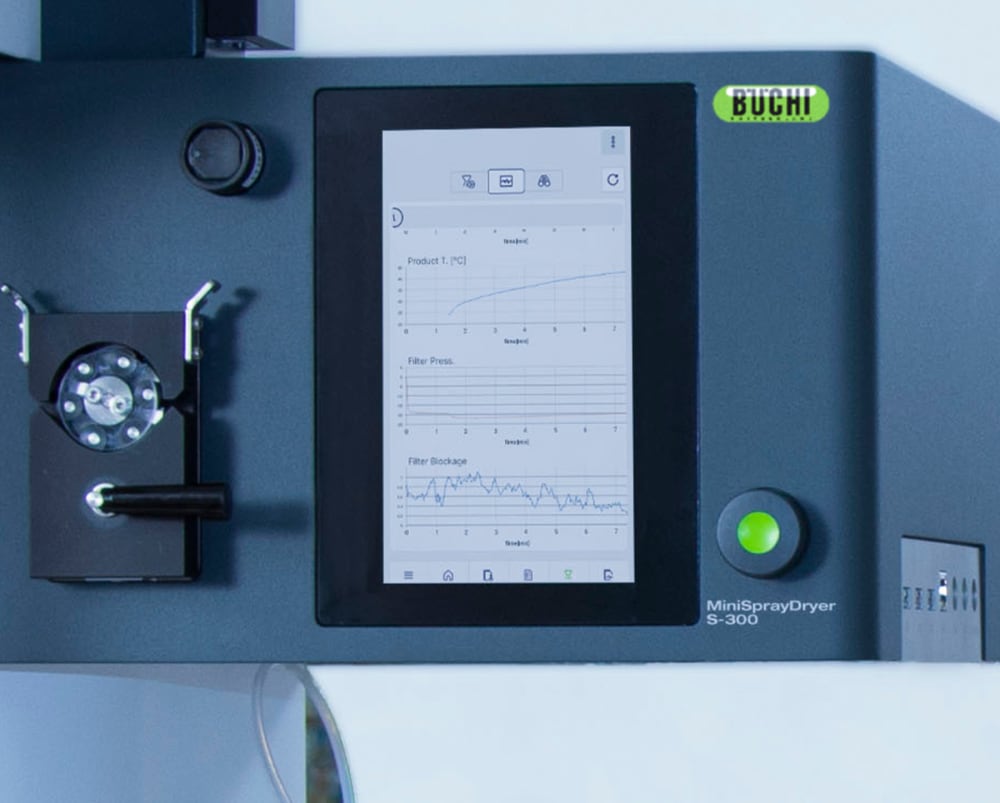
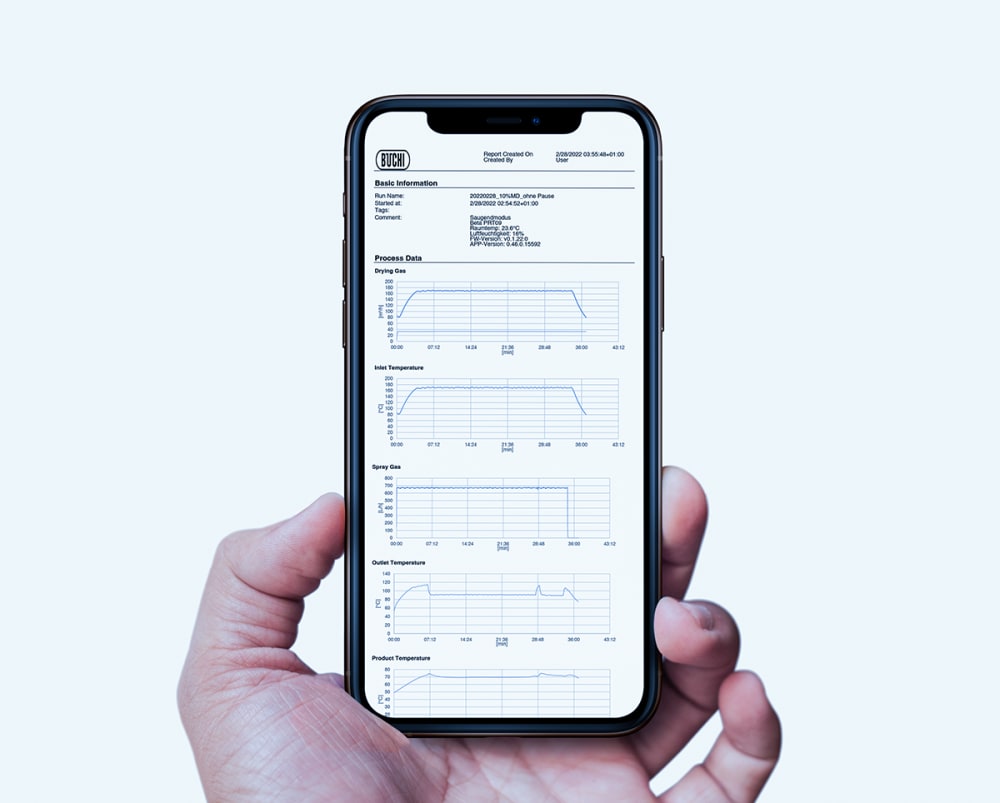
- ミニスプレードライヤー S-300による全ての運転記録は、装置に記録・保存されます。ボタンを押すだけで処理データを含むPDFレポートや.csvファイルが作成されます。
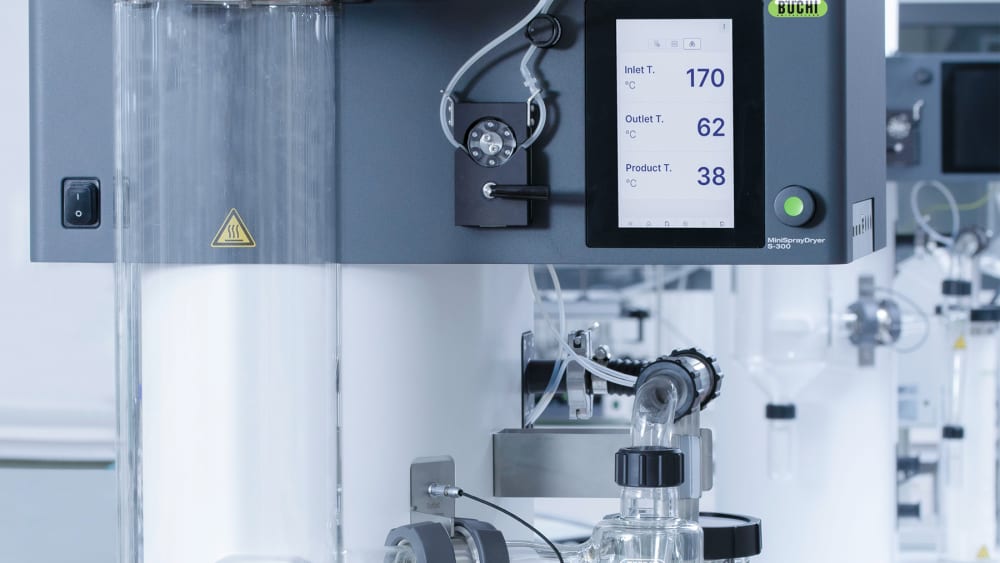
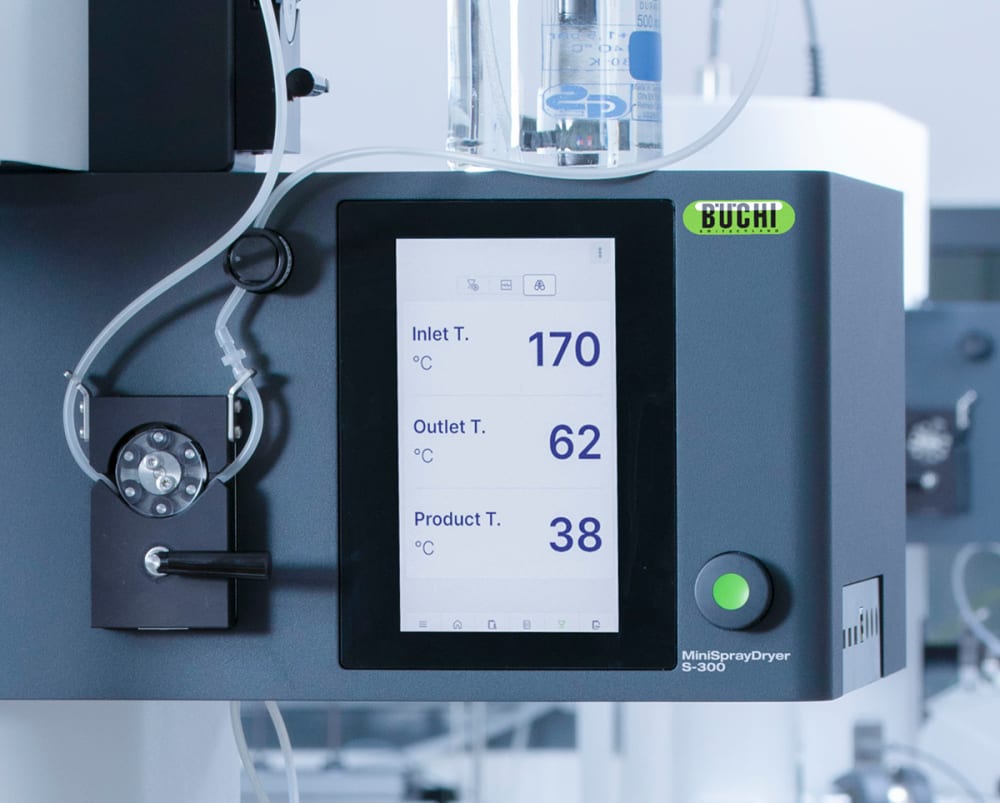
- ミニスプレードライヤー S-300は、出口温度と最終製品温度の両方を監視できるので試料への熱影響についてより多くの情報を得る事ができます。この情報は、噴霧乾燥において特に熱に敏感な試料を保護するために役立ちます。
- ミニスプレードライヤー S-300では、ガスの噴霧、乾燥用の熱風、ポンプ速度などすべてのパラメータが動作設定値ではなく実測値で管理されシステムが自動的に調節します。この機能により、処理の再現性を最大限に高めることができます。
- ミニスプレードライヤー S-300はイナートループ S-395と組み合わせることで、有機溶媒を含む試料のスプレードライを安全に行うことができます。不活性な窒素ガスを乾燥ガスとして循環させ、溶媒の蒸気は冷却凝縮して回収します。安全のためにシステム内の酸素濃度とガス流量は常にモニタリングされます。
Compare the ミニスプレードライヤー S-300
関連パーツ/アクセサリー
ダウンロード
- Technical Data Sheet Mini Spray Dryer S-300(pdf)
- Product Brochure Mini Spray Dryer S-300 en(pdf)
- Product Brochure Pharma and Chemistry en(pdf)
- Operation Manual Mini Spray Dryer S-300 en(pdf)
- Installation Manual Mini Spray Dryer S-300 in closed mode with Inert Loop(pdf)
- Installation Manual Mini Spray Dryer S-300 in closed mode with Dehumidifier and Inert Loop(pdf)
- Installation Manual Mini Spray Dryer S-300 in open suction mode(pdf)
- Installation Manual Mini Spray Dryer S-300 in open pressure mode(pdf)
- Configuration guide S-300(pdf)
- Pre-Installation Checklist Mini Spray Dryer S-300(pdf)
関連製品
関連のコース&トレーニング
アプリケーション
あらゆる種類の応用に対応できる比類なき柔軟性
Batteries
Laboratory-scale spray drying is a valuable technique in battery research for the fabrication of electrode materials. It enables precise control over particle size and morphology, resulting in electrodes with optimized electrochemical performance. Spray drying allows for the production of fine and uniform particles, contributing to the development of high-performance batteries. This method facilitates the development of electrode materials with enhanced properties, such as improved conductivity and electrochemical stability. By employing laboratory-scale spray drying in battery research, scientists can advance energy storage technologies and develop more efficient and reliable batteries for various applications.
Biotech
Applications: Cells, bacteria and protein encapsulation, cell transplantation, biotransformation Methods: Drying, encapsulation of liquids, Encapsulation of solids, Micronization, Cell encapsulation Instruments used: Mini Spray Dryer S-300, Nano Spray Dryer B-90, Encapsulator B-390 / B-395, Lyovapor L-200 / L-300
Chemicals / Materials
Laboratory-scale spray drying is a versatile and efficient method for producing a wide range of materials in the chemicals and materials science field. In recent years, notable trends have emerged, including the application of spray drying for nano materials, paints and coatings, and catalysts. One trend is the use of laboratory-scale spray drying in the synthesis of nano materials. This technique enables the production of nanoparticles and nanostructured materials with controlled size, morphology, and composition. By tailoring these properties, researchers can develop advanced materials with improved mechanical strength, enhanced conductivity, and tailored surface functionalities. Spray drying also finds application in the production of paints and coatings. By producing fine and uniform particles, spray drying contributes to the desired properties of coatings, such as improved color, durability, and film formation. This trend leads to the development of high-quality coatings with enhanced performance and functionality. Furthermore, laboratory-scale spray drying plays a role in the development of catalysts. By controlling particle size, composition, and surface area, spray drying allows for the design and optimization of catalysts for efficient chemical transformations and environmental applications. In summary, laboratory-scale spray drying in the chemicals and materials science field is witnessing trends in nano materials, paints and coatings, and catalysts. These trends contribute to the development of advanced materials, high-performance coatings, and efficient catalysts, driving innovation in various industries.
Cosmetics
Applications: Cosmetics, fragrances Methods: Drying, encapsulation of liquids, Encapsulation of solids, Micronization Instruments used: Mini Spray Dryer S-300, Encapsulator B-390 / B-395, Lyovapor L-200 / L-300
Food
Applications: Encapsulation of additives, controlled release, nutraceuticals, functional foods, flavors, vitamins, proteins, probiotic bacteria, juice concentrate, milk powder Methods: Drying, encapsulation of liquids, Encapsulation of solids, Micronization Instruments used: Mini Spray Dryer S-300, Encapsulator B-390 / B-395, Lyovapor L-200 / L-300
Pharma
Laboratory-scale spray drying is a vital process in the pharmaceutical industry, used for the formulation and development of various drugs and medications. It involves converting liquid solutions or suspensions into dry powders through atomization and rapid evaporation. This technique offers several benefits, including improved stability, enhanced bioavailability, and ease of handling. In recent years, several notable trends have emerged in laboratory-scale spray drying within the pharmaceutical sector. One significant trend is the use of spray drying for the production of solid dispersions. Solid dispersions are formulations where the drug is dispersed in a solid matrix, enhancing its solubility and dissolution rate. Spray drying enables the preparation of solid dispersion powders with uniform drug distribution, leading to improved drug delivery and efficacy. Another trend is the development of inhalable drugs using spray drying. This technique allows for the production of dry powder formulations suitable for inhalation, facilitating targeted delivery to the respiratory system. Inhalable drugs offer advantages in the treatment of respiratory diseases, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Taste masking is another important application of laboratory-scale spray drying. By encapsulating drugs with unpleasant taste profiles in taste-masking particles, the palatability of oral formulations can be improved. Spray drying enables the encapsulation of drugs within taste-masking coatings, leading to better patient compliance, particularly for pediatric and geriatric populations. Furthermore, laboratory-scale spray drying is increasingly employed for the development of controlled-release formulations. By incorporating drugs into sustained-release matrices or encapsulating them within microspheres or nanoparticles, spray drying allows for the controlled release of drugs over an extended period. This enables optimized drug dosage regimens and improved patient convenience. In conclusion, laboratory-scale spray drying in the pharmaceutical area is witnessing several significant trends, including the production of solid dispersions, inhalable drugs, taste-masking formulations, and controlled-release systems. These trends contribute to the development of novel drug formulations with enhanced solubility, targeted delivery, improved patient compliance, and optimized drug release profiles.