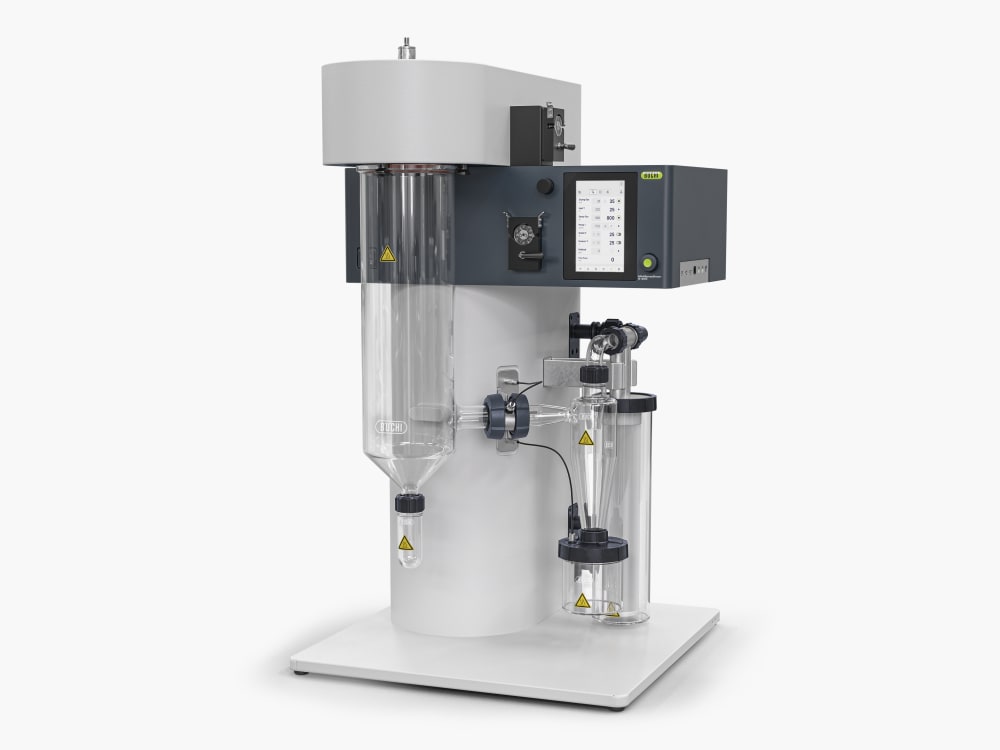
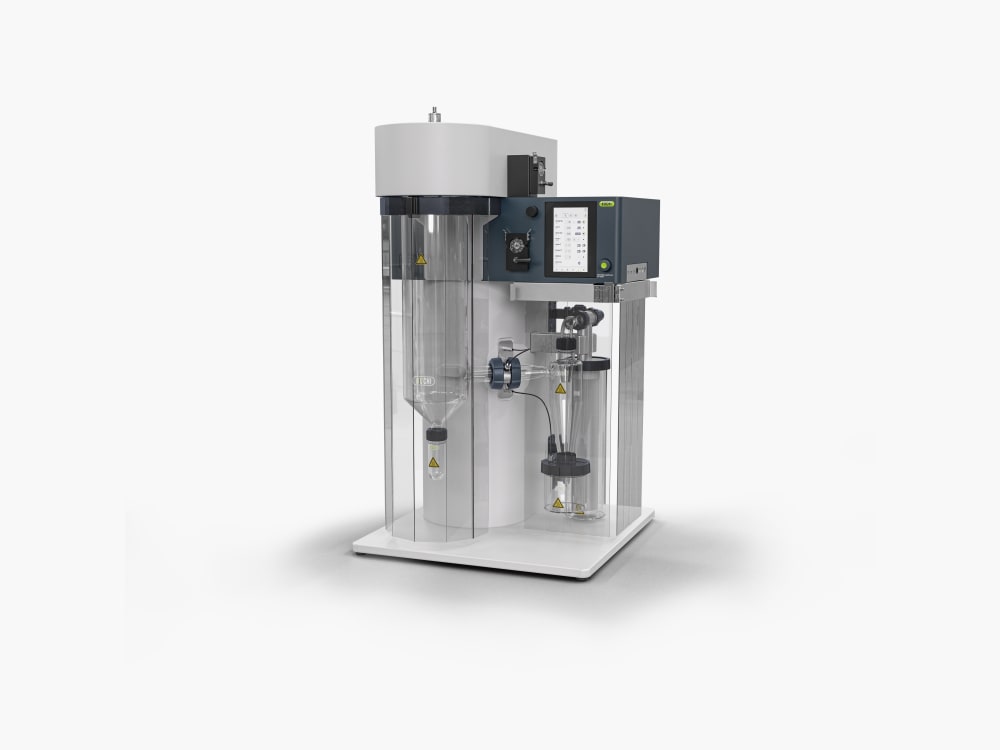
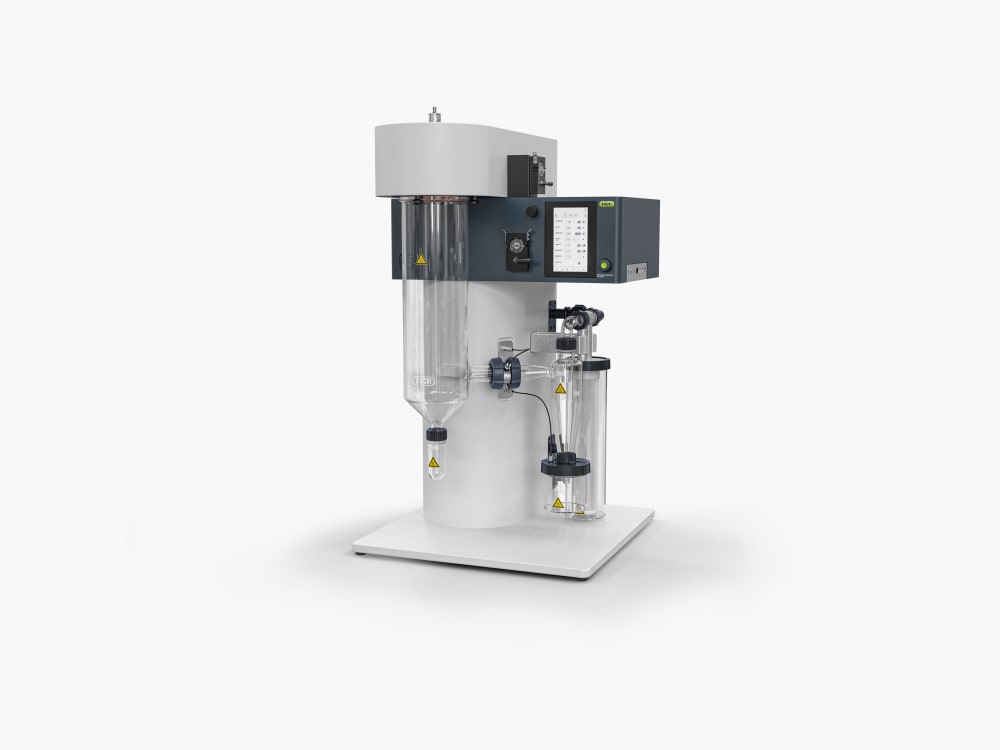
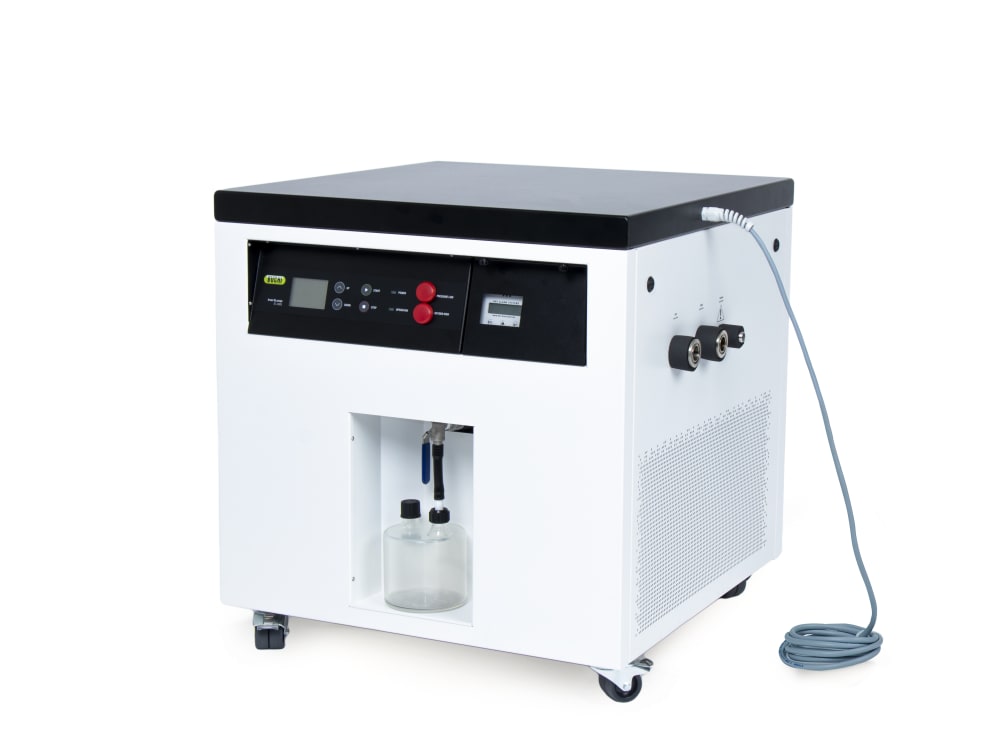
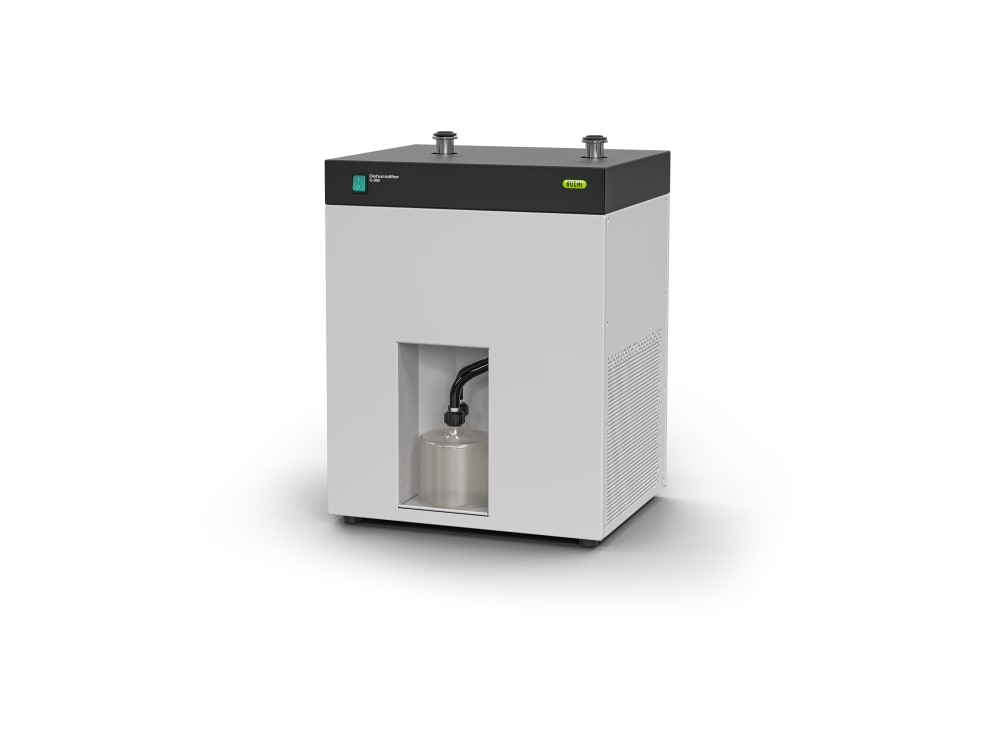
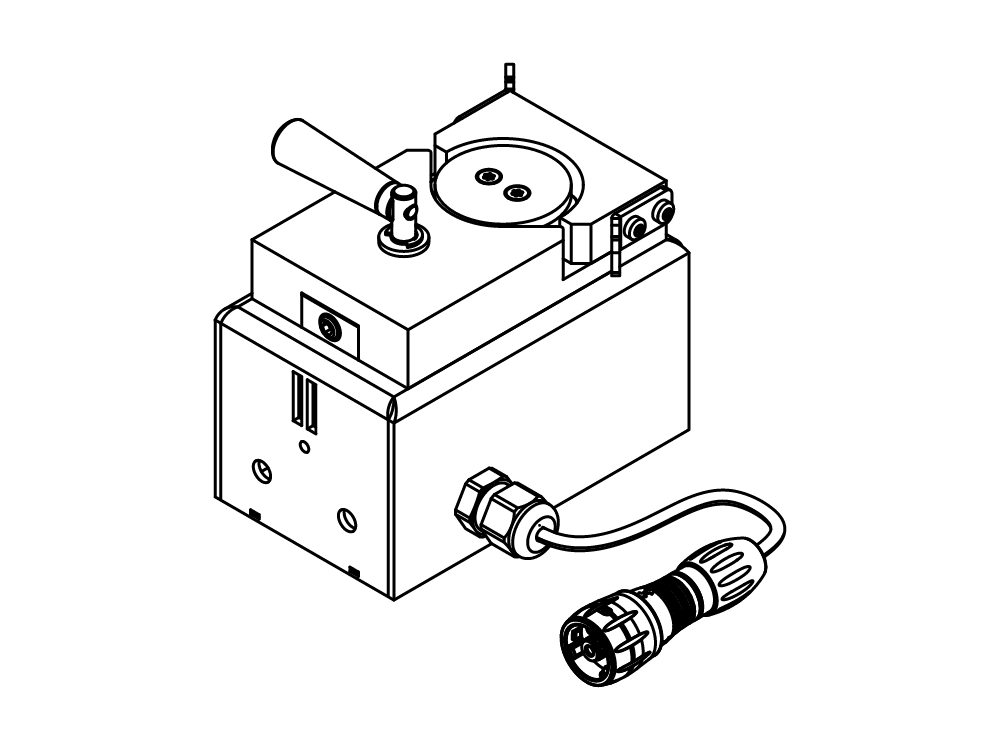
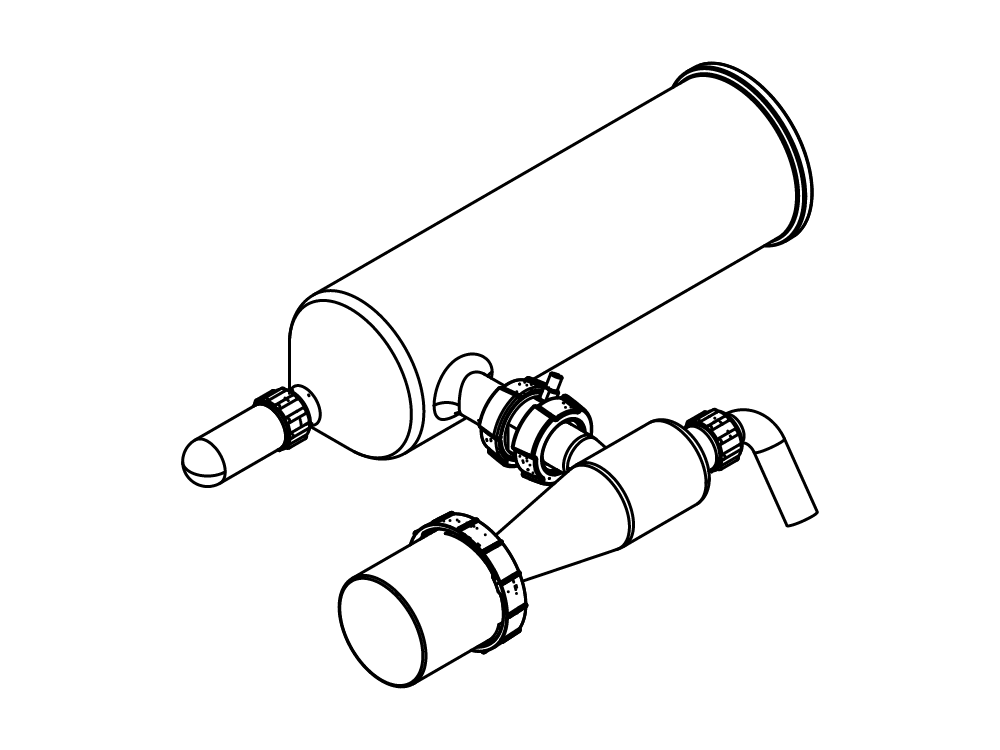
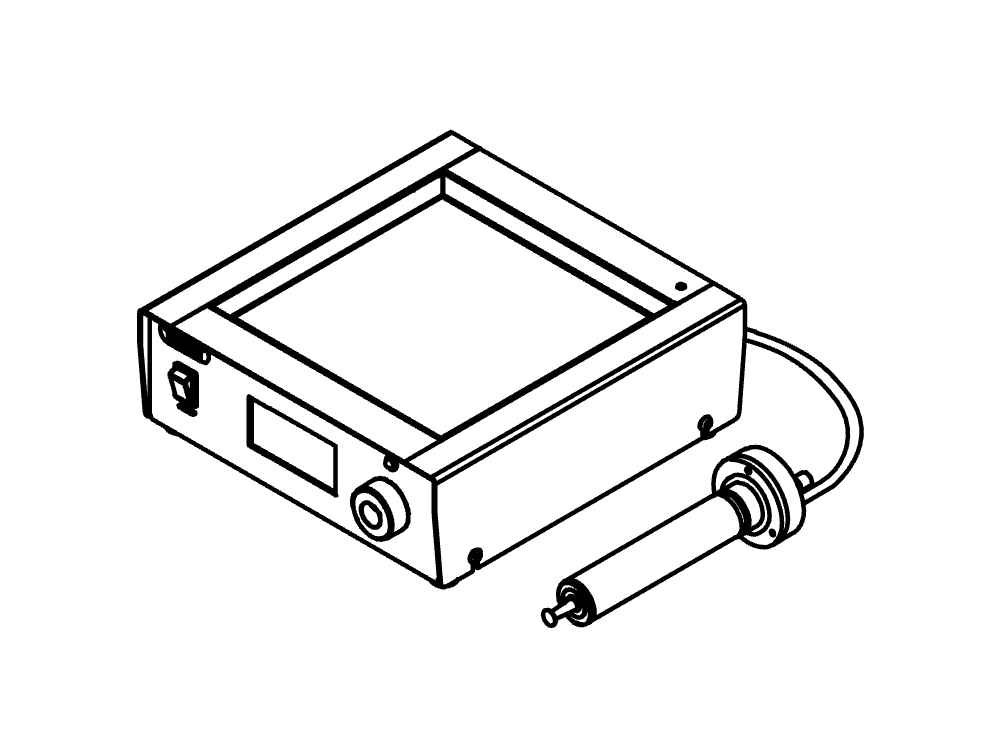
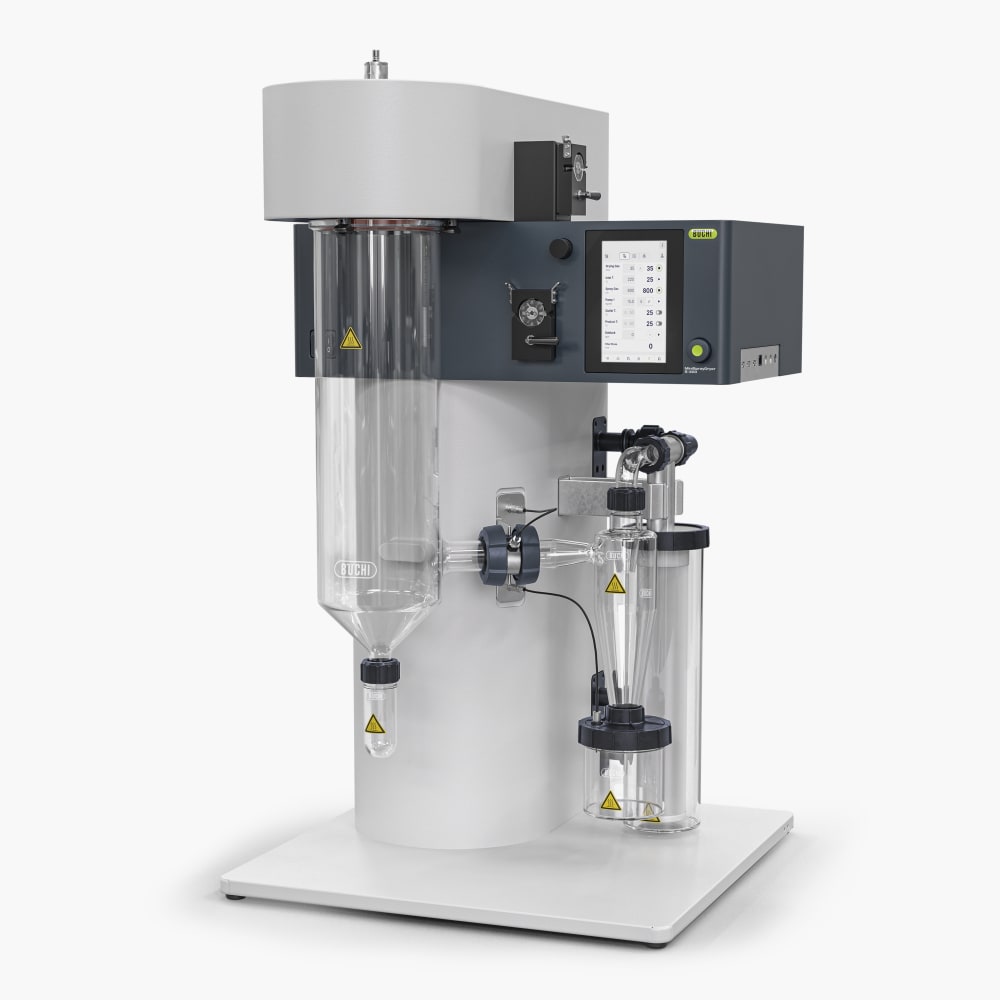
小型喷雾干燥仪 S-300
下一代实验室喷雾干燥仪
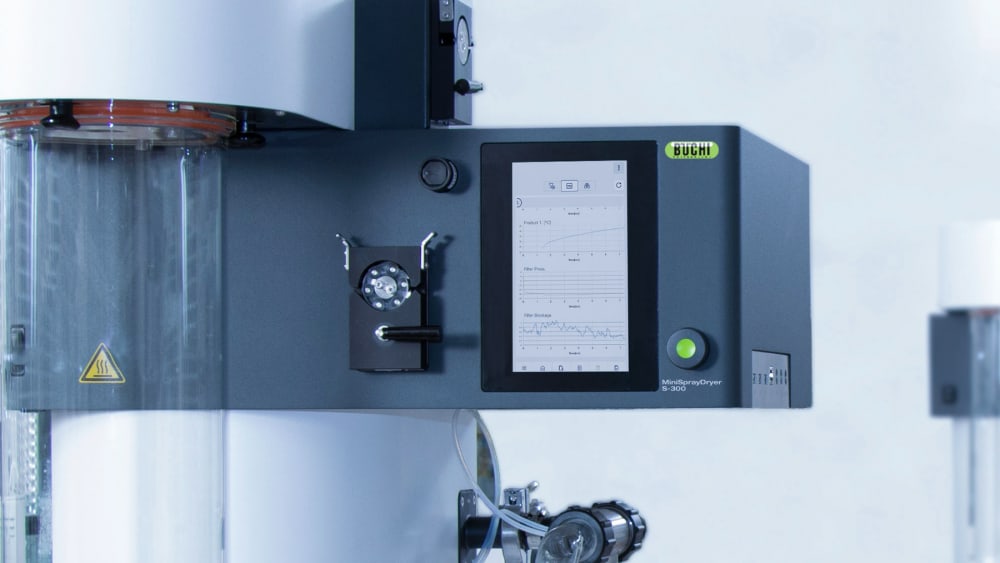
凭借小型喷雾干燥仪 S-300,BUCHI 巩固了其 40 多年来作为全球市场领导者的地位。实验室喷雾干燥仪融合卓越的产品设计与独特的仪器功能,可为用户提供极佳的使用体验。

特性
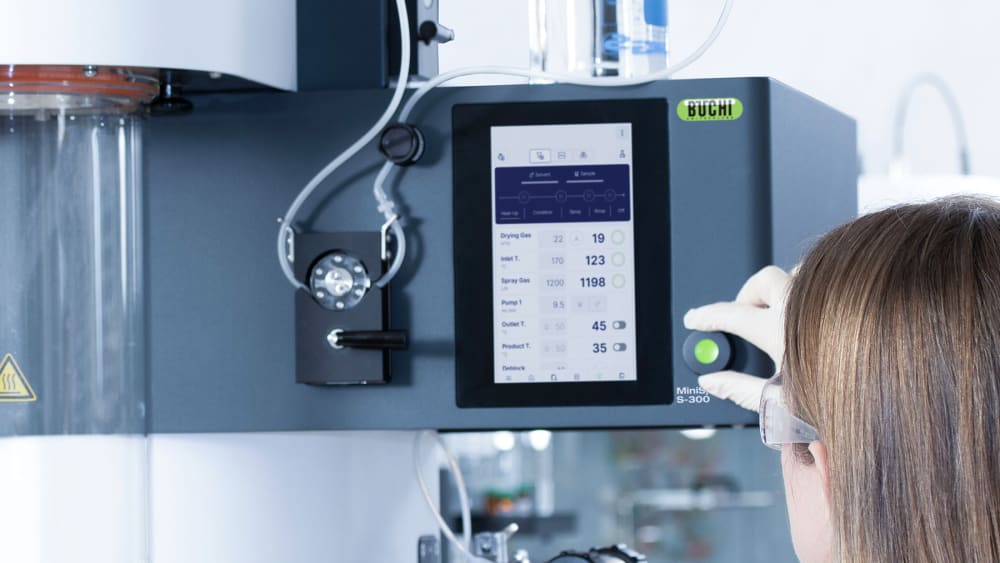
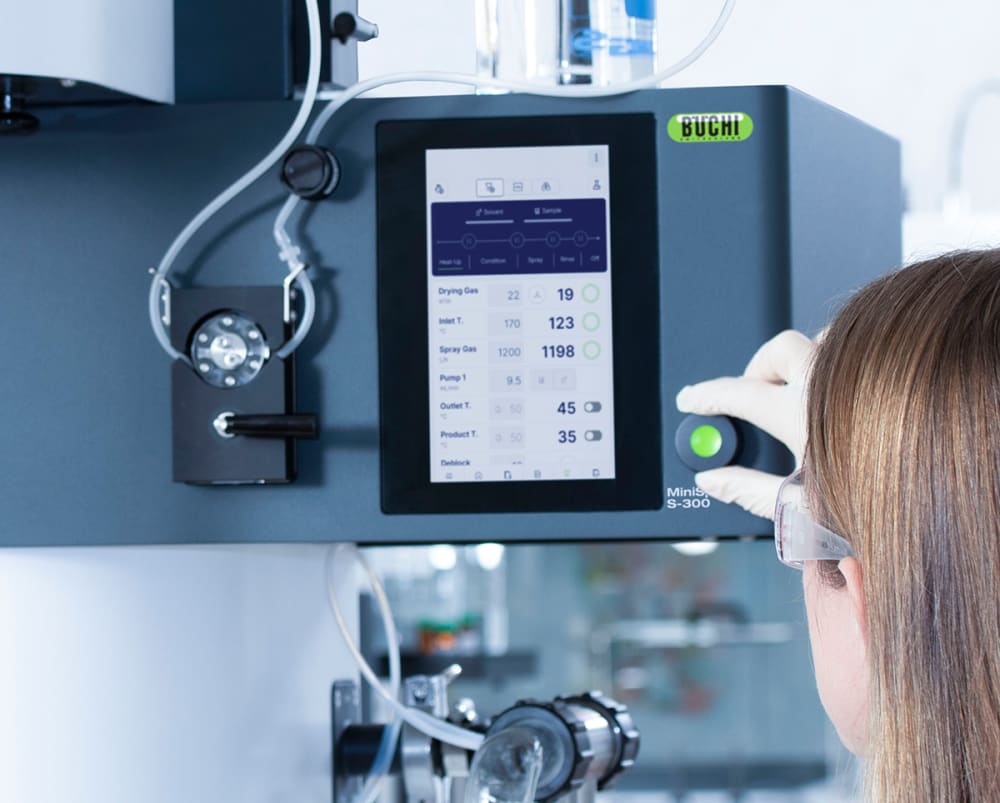
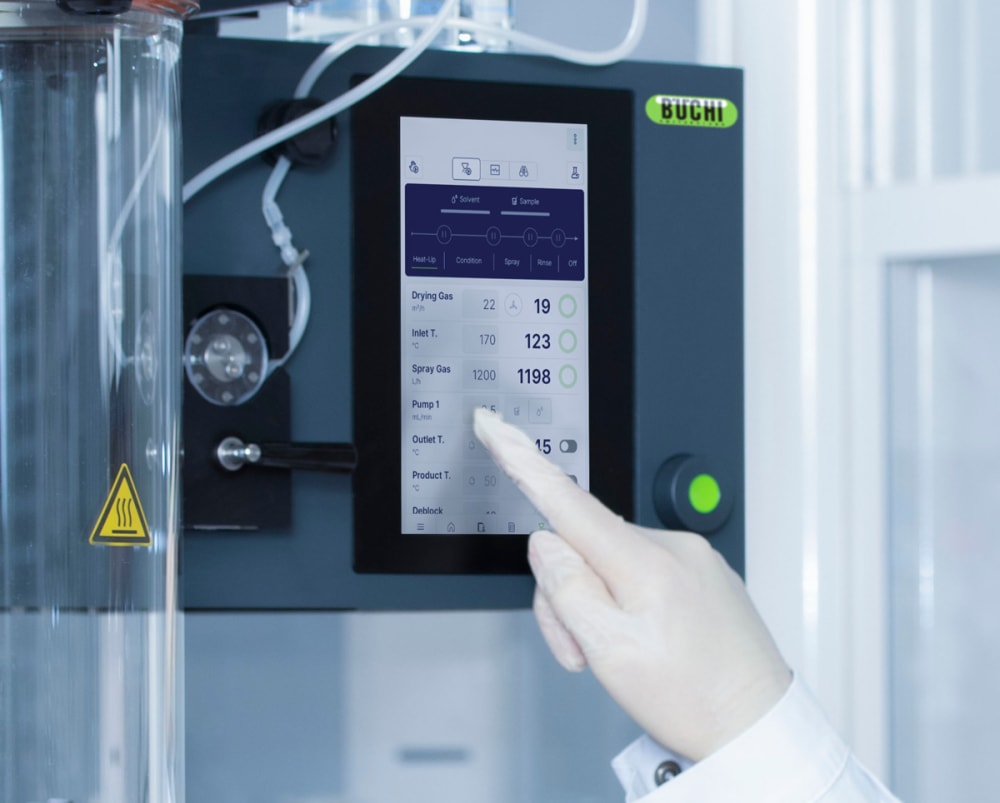
- 随时随地控制或监查小型喷雾干燥仪 S-300。您可以通过任何移动设备或计算机上的应用程序,访问实验室喷雾干燥仪的所有用户界面。您可以借助远程控制选项,进行灵活的时间管理,并对过程更改作出快速反应。
- 凭借 40 多年的实验室规模喷雾干燥经验,BUCHI 积累了丰富的应用知识。在科学图书馆翻阅数以千计的关于 BUCHI 喷雾干燥仪的出版文献,或者浏览我们的在线喷雾干燥应用数据库,查找符合您需求的应用。小型喷雾干燥仪 S-300 可帮您重现使用 BUCHI 旧型号实验室喷雾干燥仪获得的结果。您可快速、无缝地转移到新仪器上,期间不会丢失任何有价值的工作成果。
- 您可通过自动模式,对高级小型喷雾干燥仪 S-300 进行编程,使其自动按您的方法运行。实验室喷雾干燥仪可以加热、调节出口温度,喷洒纯溶剂,喷洒样品,再次喷洒溶剂,并在处理完样品后关闭。自动模式可以提高流程的时间效率,尤其是重复性任务。
- 带有导电涂层的旋风分离器可以让您的样品不那么容易粘附在容器壁上,从而减少实验室喷雾干燥过程中的样品损失。
- 通过将运行的程序保存为方法,以便以后重复这些方法来节省时间、减少麻烦。您还可以对样品序列进行编程,然后在小型喷雾干燥仪 S-300 上依次运行,过程方便快捷。
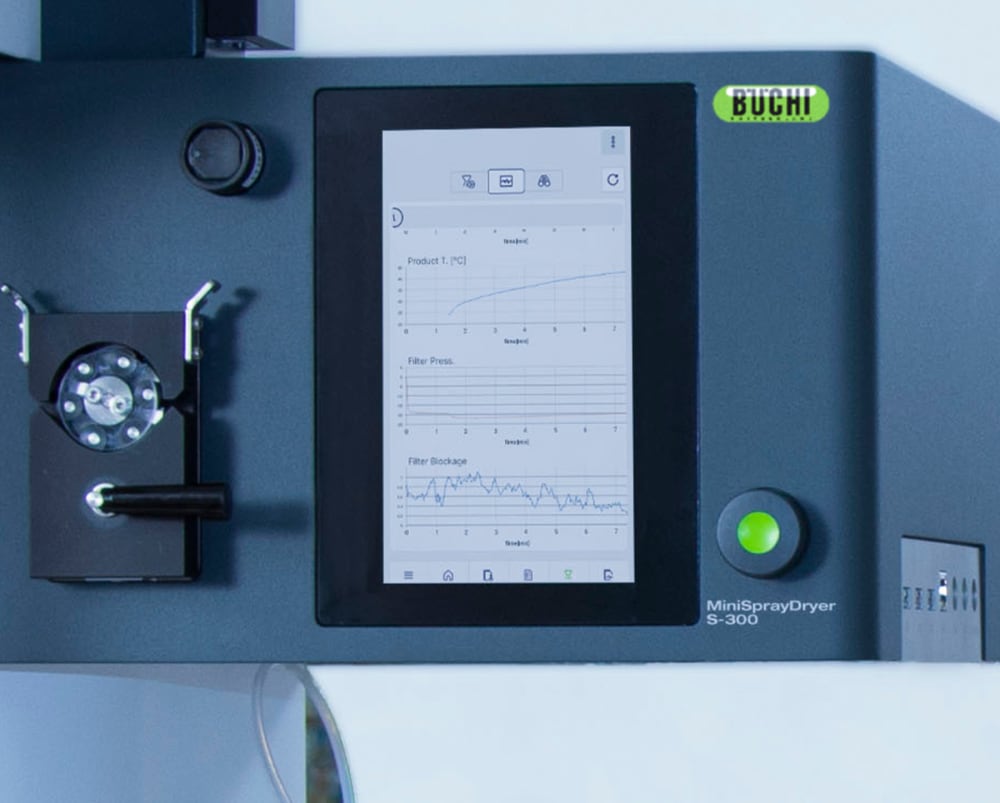
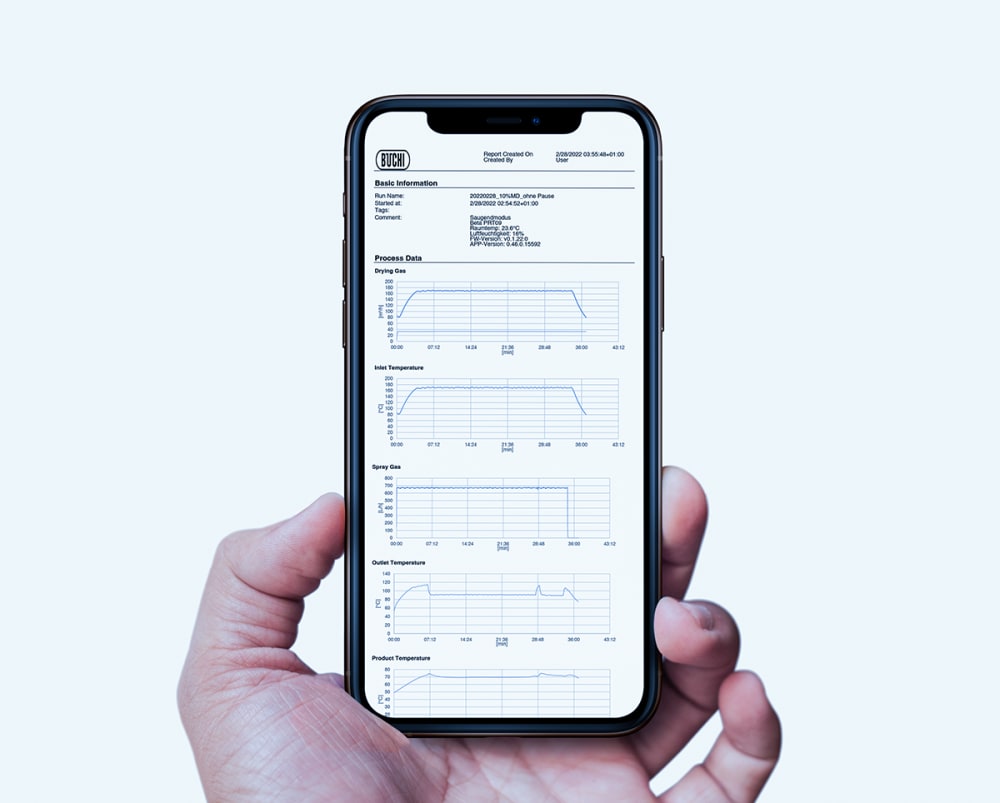
- 您在小型喷雾干燥仪 S-300 上执行的所有运行都会记录并保存在仪器上。只需按一下按钮,即可轻松生成包含过程数据的 PDF 报告或者 .csv 格式文件。
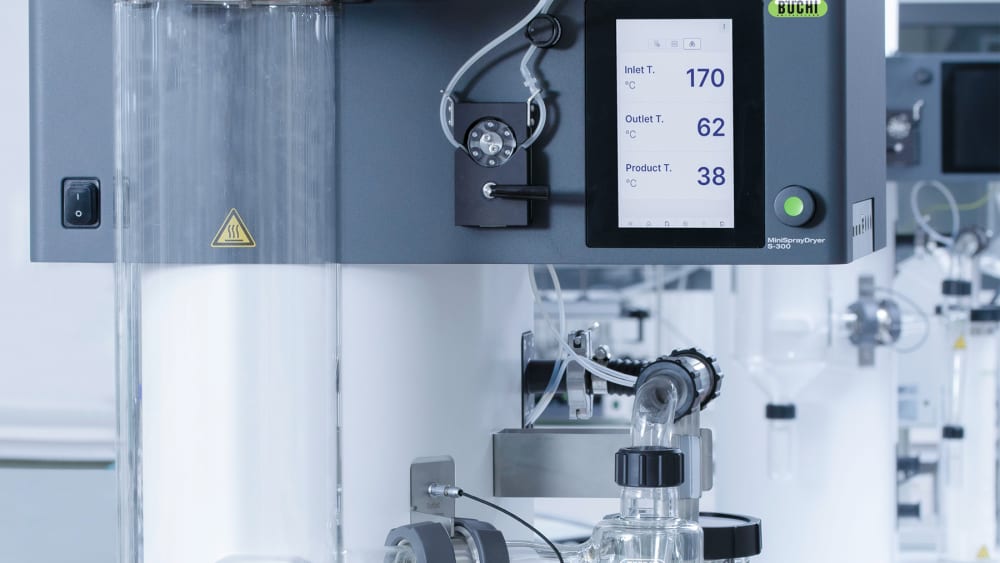
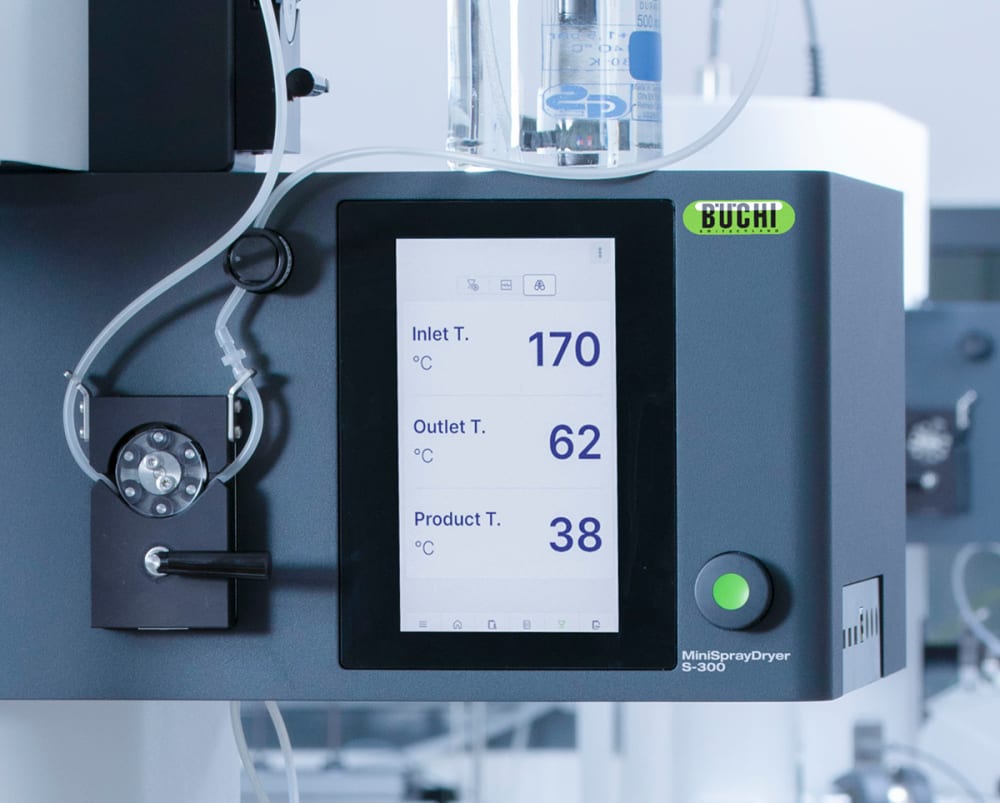
- 为了向您提供有关样品热影响的更多信息,小型喷雾干燥仪 S-300 允许您监控出口温度和最终产品温度。此信息可以帮助您更好地保护样品,尤其是在喷雾干燥热敏样品时。
- 小型喷雾干燥仪 S-300 中的所有参数,例如喷雾气流、干燥气流和泵速,均以 SI 值形式提供,并由系统自动调节。这些功能可最大限度提高上述过程的重现性。
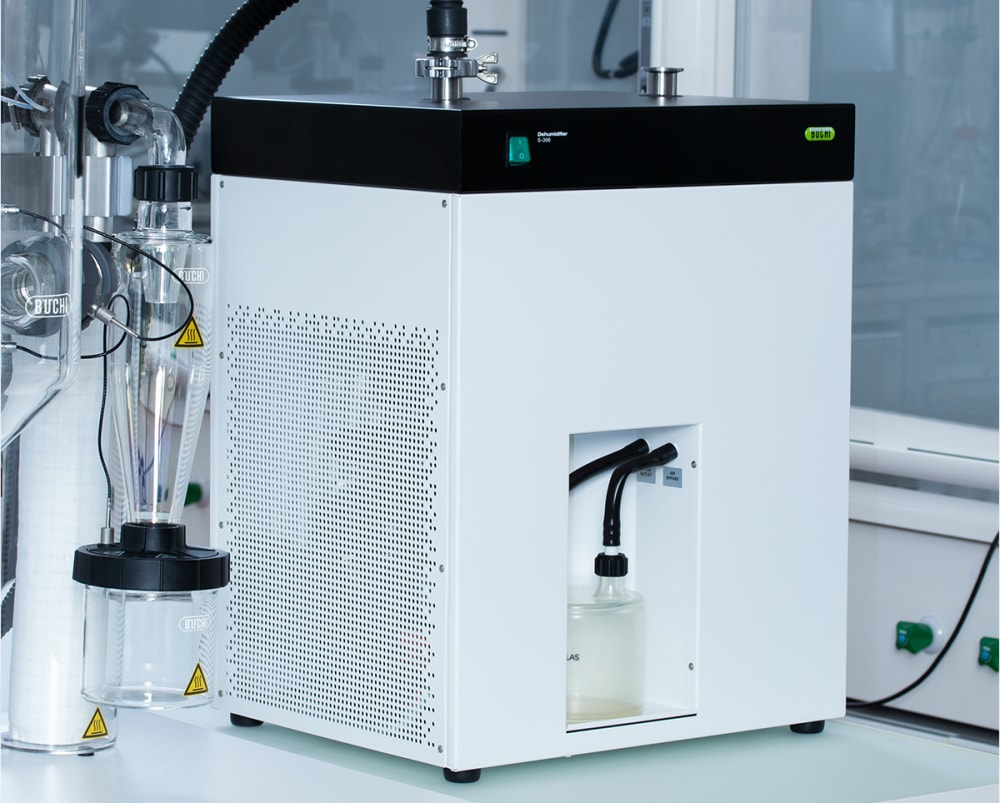
- 小型喷雾干燥仪 S-300 可和惰性气体循环装置 S-395 结合使用,安全处理含有机溶剂的样品。氮气干燥气体会循环使用,而溶剂则会作为冷凝液收集起来。为了保护您的安全,会持续监控系统中的氧气含量和气体流量。
Compare the 小型喷雾干燥仪 S-300
相关部件&附件
下载
- Technical Data Sheet Mini Spray Dryer S-300(pdf)
- Product Brochure Mini Spray Dryer S-300 en(pdf)
- Product Brochure Pharma and Chemistry en(pdf)
- Operation Manual Mini Spray Dryer S-300 en(pdf)
- Installation Manual Mini Spray Dryer S-300 in closed mode with Inert Loop(pdf)
- Installation Manual Mini Spray Dryer S-300 in closed mode with Dehumidifier and Inert Loop(pdf)
- Installation Manual Mini Spray Dryer S-300 in open suction mode(pdf)
- Installation Manual Mini Spray Dryer S-300 in open pressure mode(pdf)
- Configuration guide S-300(pdf)
- Pre-Installation Checklist Mini Spray Dryer S-300(pdf)
相关仪器
相关的课程和培训
应用
可适合各种应用,具有无与伦比的灵活性
Batteries
Laboratory-scale spray drying is a valuable technique in battery research for the fabrication of electrode materials. It enables precise control over particle size and morphology, resulting in electrodes with optimized electrochemical performance. Spray drying allows for the production of fine and uniform particles, contributing to the development of high-performance batteries. This method facilitates the development of electrode materials with enhanced properties, such as improved conductivity and electrochemical stability. By employing laboratory-scale spray drying in battery research, scientists can advance energy storage technologies and develop more efficient and reliable batteries for various applications.
Biotech
Applications: Cells, bacteria and protein encapsulation, cell transplantation, biotransformation Methods: Drying, encapsulation of liquids, Encapsulation of solids, Micronization, Cell encapsulation Instruments used: Mini Spray Dryer S-300, Nano Spray Dryer B-90, Encapsulator B-390 / B-395, Lyovapor L-200 / L-300
Chemicals / Materials
Laboratory-scale spray drying is a versatile and efficient method for producing a wide range of materials in the chemicals and materials science field. In recent years, notable trends have emerged, including the application of spray drying for nano materials, paints and coatings, and catalysts. One trend is the use of laboratory-scale spray drying in the synthesis of nano materials. This technique enables the production of nanoparticles and nanostructured materials with controlled size, morphology, and composition. By tailoring these properties, researchers can develop advanced materials with improved mechanical strength, enhanced conductivity, and tailored surface functionalities. Spray drying also finds application in the production of paints and coatings. By producing fine and uniform particles, spray drying contributes to the desired properties of coatings, such as improved color, durability, and film formation. This trend leads to the development of high-quality coatings with enhanced performance and functionality. Furthermore, laboratory-scale spray drying plays a role in the development of catalysts. By controlling particle size, composition, and surface area, spray drying allows for the design and optimization of catalysts for efficient chemical transformations and environmental applications. In summary, laboratory-scale spray drying in the chemicals and materials science field is witnessing trends in nano materials, paints and coatings, and catalysts. These trends contribute to the development of advanced materials, high-performance coatings, and efficient catalysts, driving innovation in various industries.
Cosmetics
Applications: Cosmetics, fragrances Methods: Drying, encapsulation of liquids, Encapsulation of solids, Micronization Instruments used: Mini Spray Dryer S-300, Encapsulator B-390 / B-395, Lyovapor L-200 / L-300
Food
Applications: Encapsulation of additives, controlled release, nutraceuticals, functional foods, flavors, vitamins, proteins, probiotic bacteria, juice concentrate, milk powder Methods: Drying, encapsulation of liquids, Encapsulation of solids, Micronization Instruments used: Mini Spray Dryer S-300, Encapsulator B-390 / B-395, Lyovapor L-200 / L-300
Pharma
Laboratory-scale spray drying is a vital process in the pharmaceutical industry, used for the formulation and development of various drugs and medications. It involves converting liquid solutions or suspensions into dry powders through atomization and rapid evaporation. This technique offers several benefits, including improved stability, enhanced bioavailability, and ease of handling. In recent years, several notable trends have emerged in laboratory-scale spray drying within the pharmaceutical sector. One significant trend is the use of spray drying for the production of solid dispersions. Solid dispersions are formulations where the drug is dispersed in a solid matrix, enhancing its solubility and dissolution rate. Spray drying enables the preparation of solid dispersion powders with uniform drug distribution, leading to improved drug delivery and efficacy. Another trend is the development of inhalable drugs using spray drying. This technique allows for the production of dry powder formulations suitable for inhalation, facilitating targeted delivery to the respiratory system. Inhalable drugs offer advantages in the treatment of respiratory diseases, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Taste masking is another important application of laboratory-scale spray drying. By encapsulating drugs with unpleasant taste profiles in taste-masking particles, the palatability of oral formulations can be improved. Spray drying enables the encapsulation of drugs within taste-masking coatings, leading to better patient compliance, particularly for pediatric and geriatric populations. Furthermore, laboratory-scale spray drying is increasingly employed for the development of controlled-release formulations. By incorporating drugs into sustained-release matrices or encapsulating them within microspheres or nanoparticles, spray drying allows for the controlled release of drugs over an extended period. This enables optimized drug dosage regimens and improved patient convenience. In conclusion, laboratory-scale spray drying in the pharmaceutical area is witnessing several significant trends, including the production of solid dispersions, inhalable drugs, taste-masking formulations, and controlled-release systems. These trends contribute to the development of novel drug formulations with enhanced solubility, targeted delivery, improved patient compliance, and optimized drug release profiles.