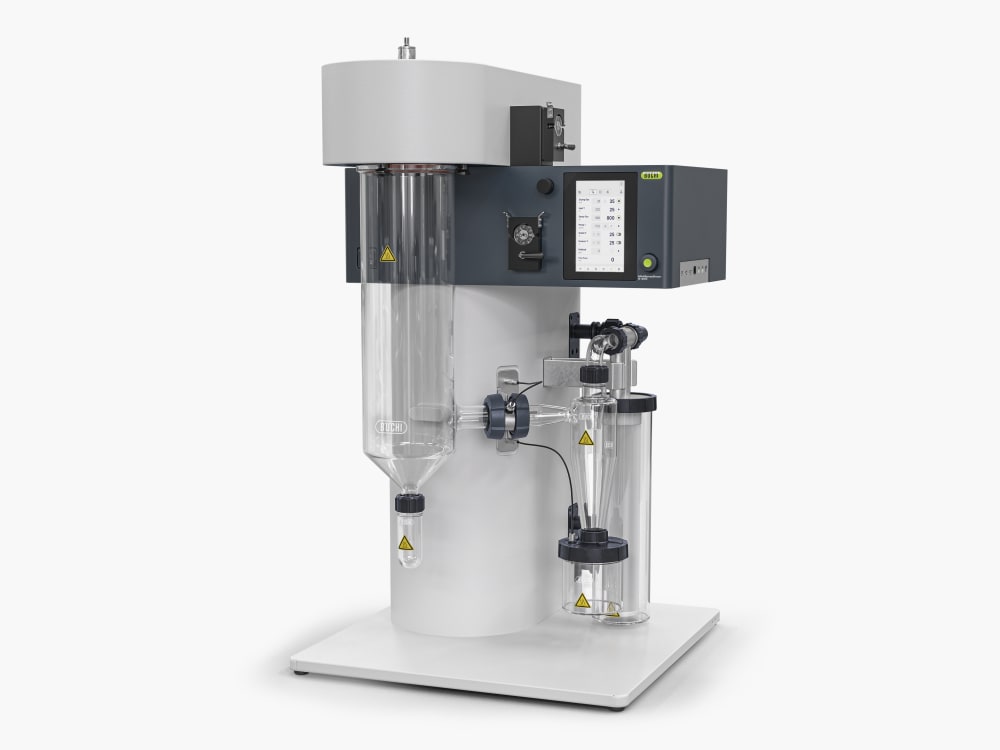
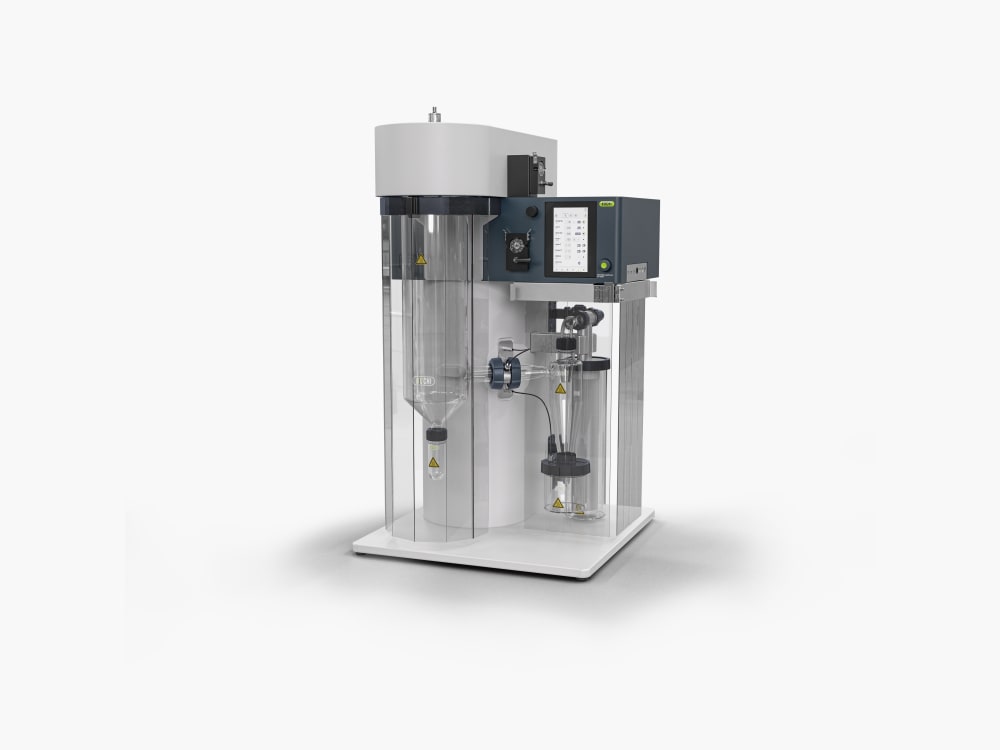
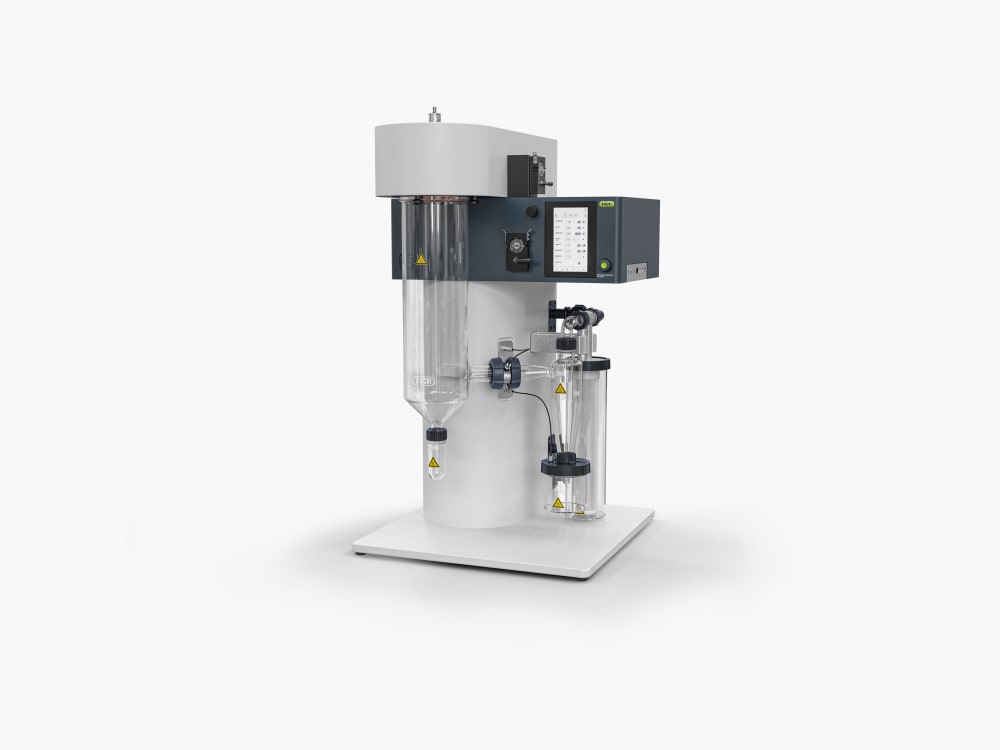
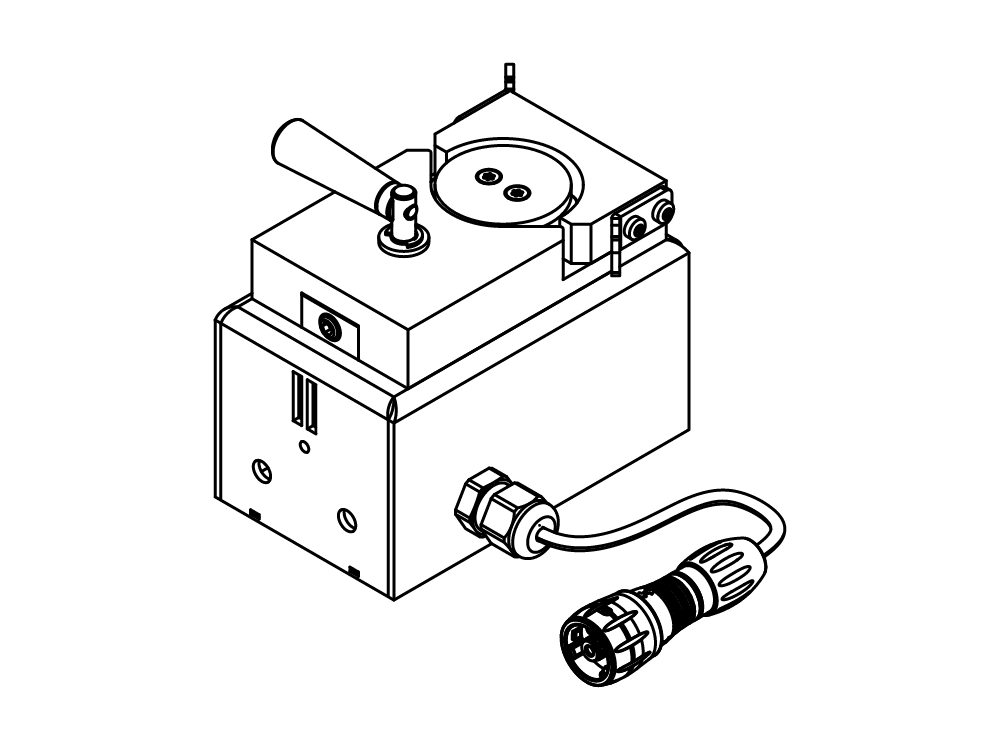
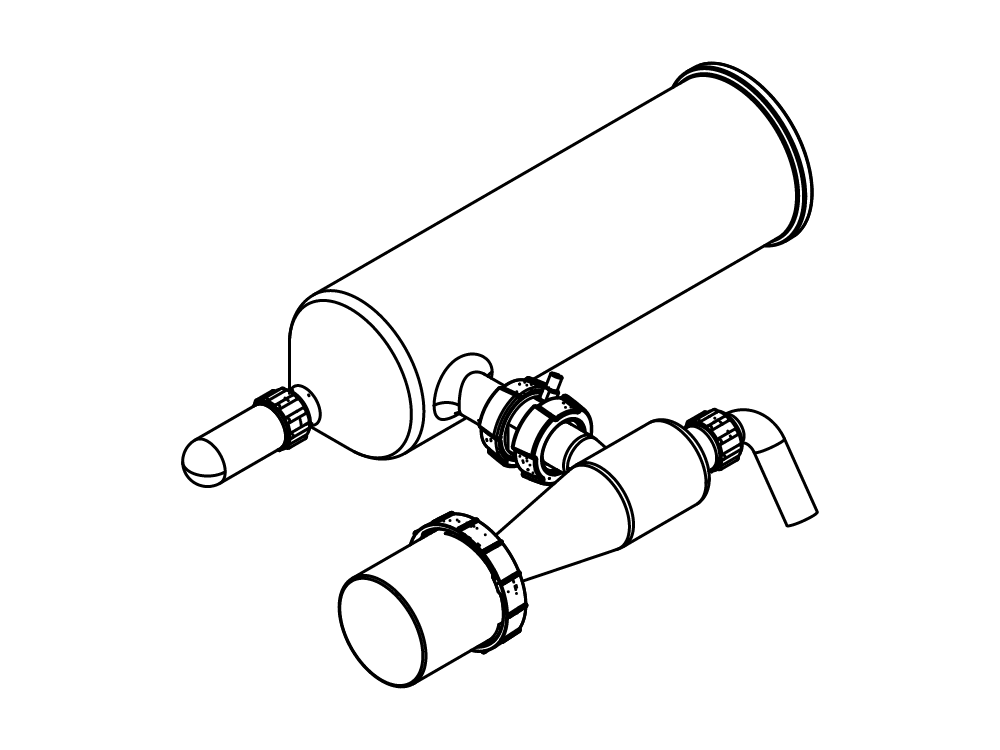
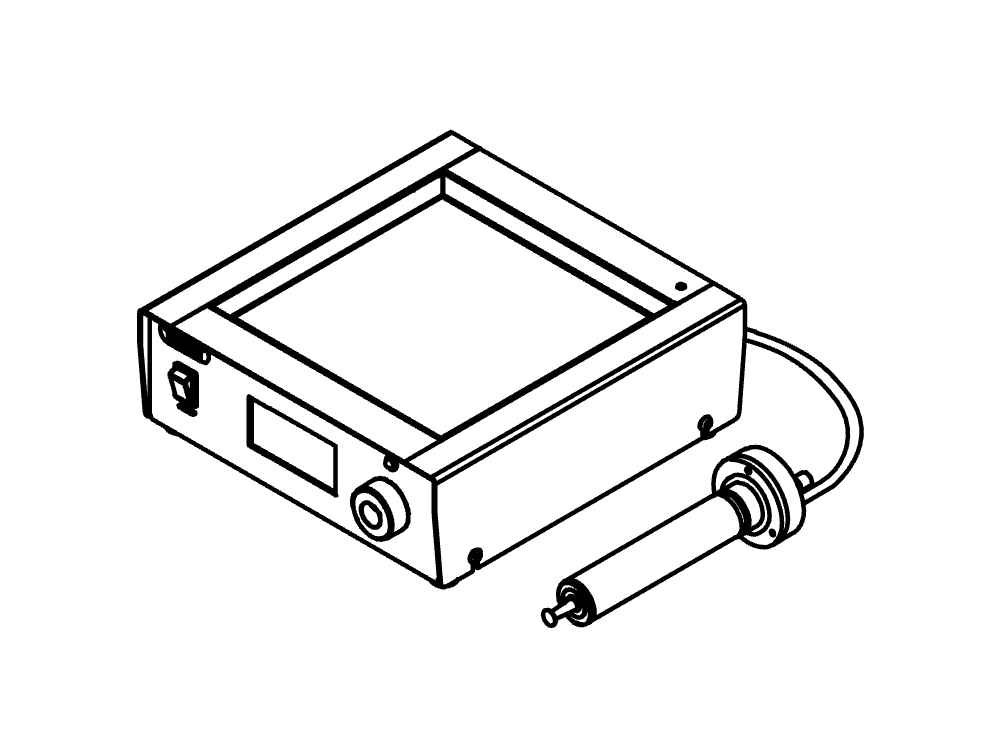
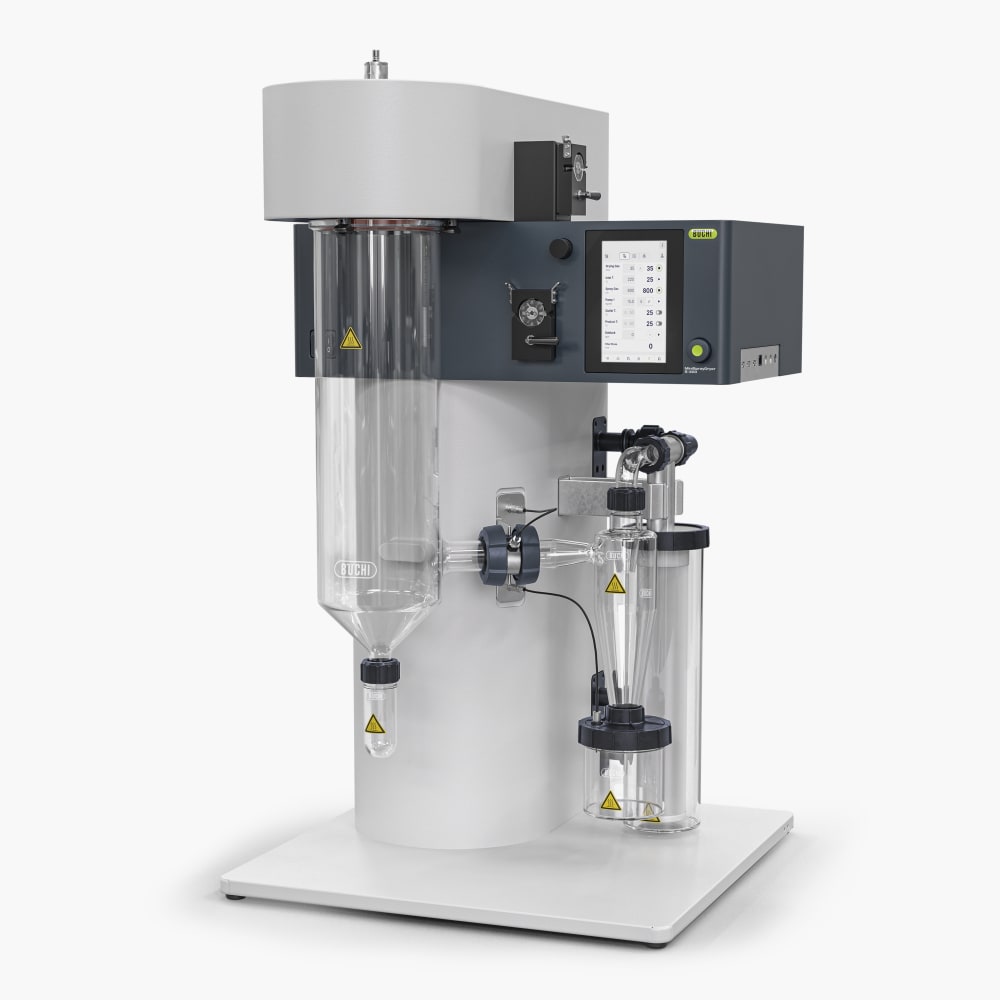
Mini Spray Dryer S-300 (소형 분무 건조기)
차세대 실험실 분무 건조기
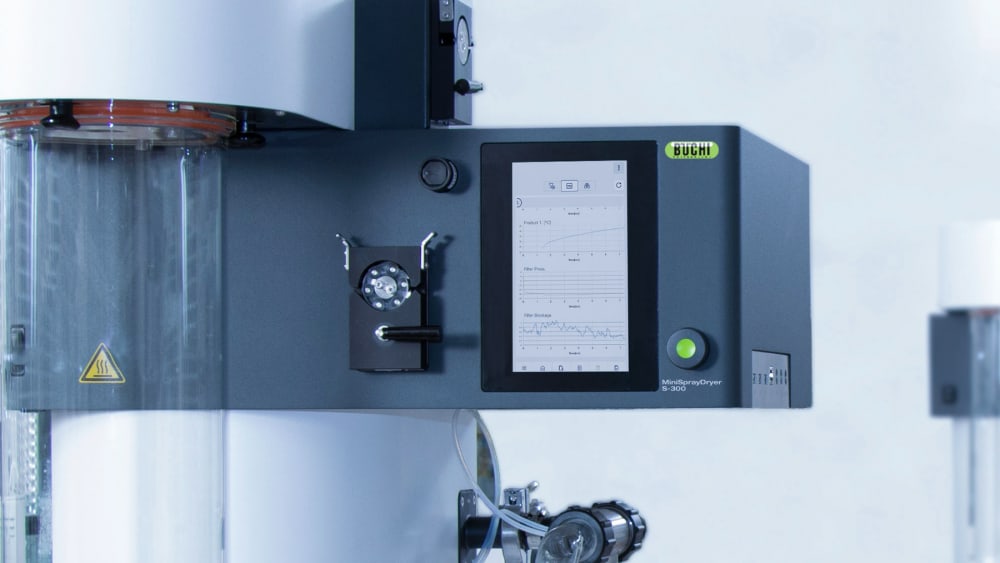
Mini Spray Dryer S-300 (소형 분무 건조기)을 통해 BUCHI는 40년 이상 글로벌 시장 리더로서의 입지를 굳건히 해왔습니다. 실험실 분무 건조기는 뛰어난 제품 디자인과 고유한 장비 기능을 결합하여 탁월한 편의성을 제공합니다.

기능
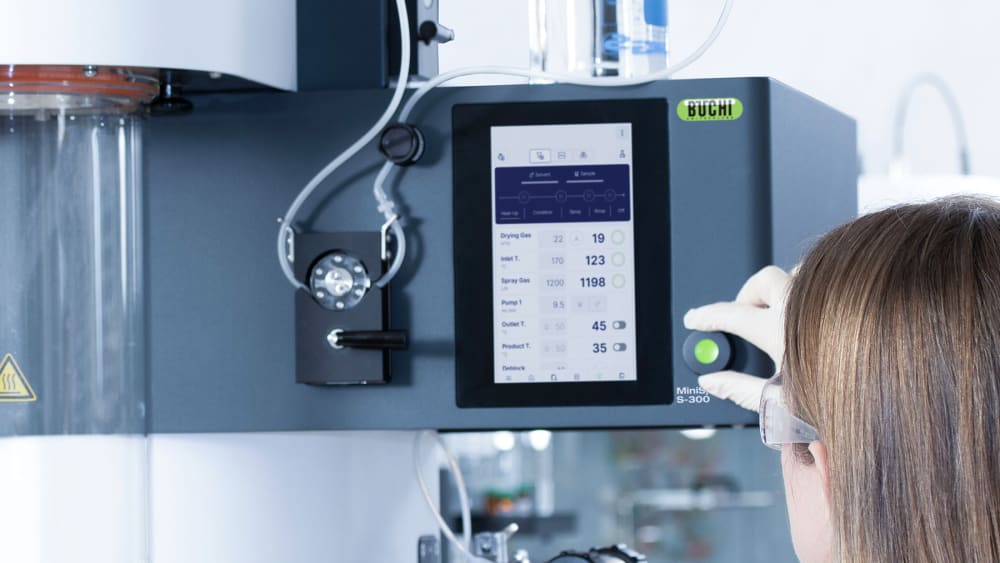
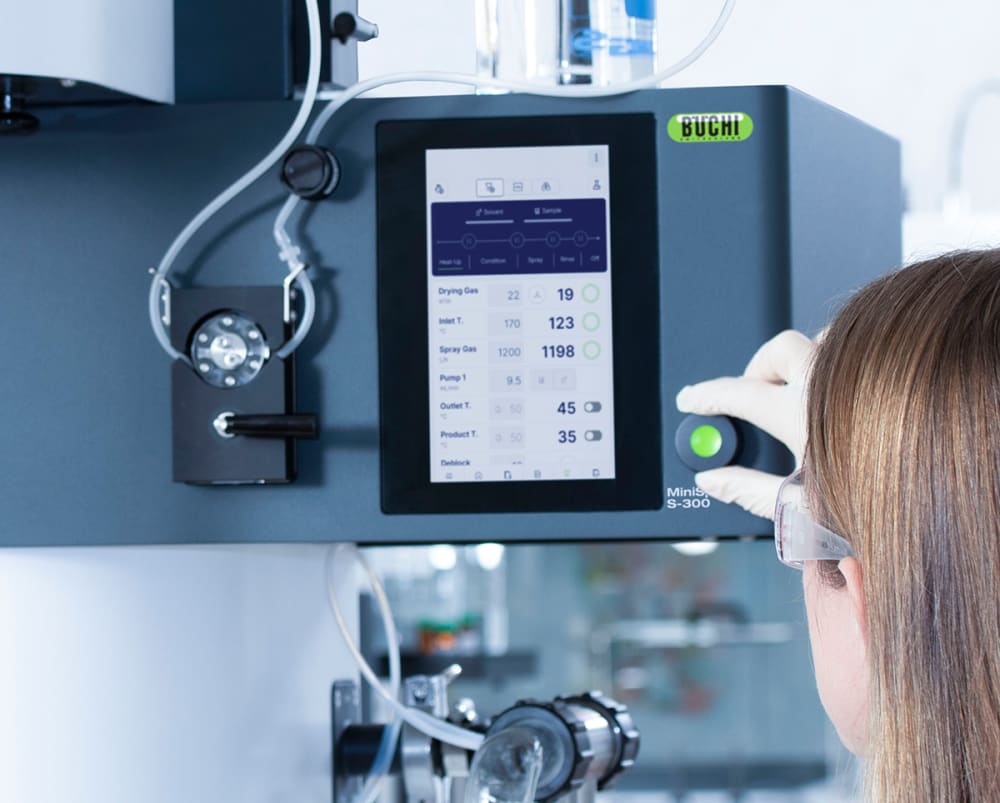
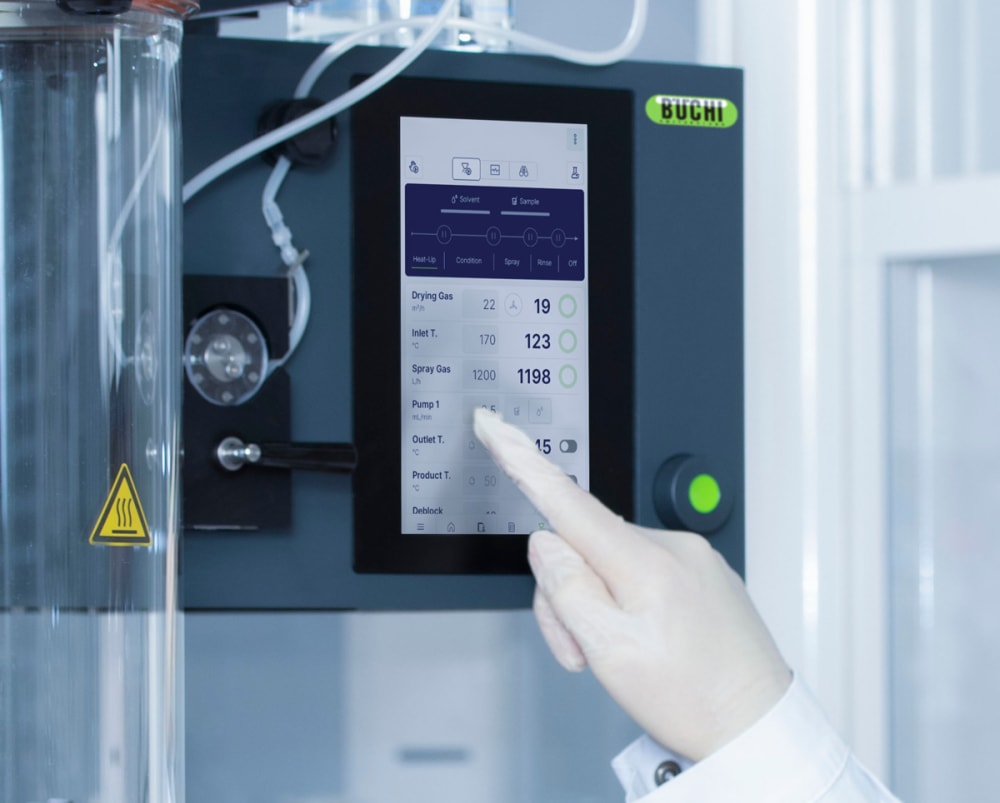
- 언제든 Mini Spray Dryer S-300 (소형 분무 건조기)을 컨트롤 및 모니터링하세요. 모든 컴퓨터와 모바일 장치의 앱은 실험실 분무건조기의 사용자 인터페이스 전체에 대한 액세스 권한을 제공합니다. 원격 제어 옵션을 사용하면 유연한 시간 관리와 프로세스 변경이 필요한 경우 빠르게 대응할 수 있습니다.
- BUCHI는 40년 이상의 실험실 분무건조 경험을 통해 광범위한 기술을 축적하였습니다. BUCHI 분무건조기가 기재된 여러 학술 문헌을 확인하거나, BUCHI 홈페이지에서 여러분 응용 분야에 맞는 다양한 분무건조 애플리케이션을 찾아보세요. Mini Spray Dryer S-300 (소형 분무 건조기)을 사용하면 기존의 BUCHI 분무건조기에서 얻은 결과를 그대로 재현할 수 있습니다. 새로운 장비로 쉽고 빠르게 데이터를 이전할 수 있어, 여러분의 소중한 연구 결과를 지킬 수 있습니다.
- 자동 모드를 사용하면 Mini Spray Dryer S-300 Advanced (소형 분무 건조기)를 프로그래밍하고 메서드를 자동으로 실행할 수 있습니다. 실험실 분무건조기의 아웃렛 온도를 예열 및 조절하고, 순수 용매 분무 후 샘플을 분무하고, 다시 순수 용매를 분무하여 샘플 처리가 완료되면 자동으로 종료됩니다. 특히, 자동 모드는 반복 작업 시 시간 효율이 매우 향상됩니다.
- 전도성 코팅이 된 사이클론으로 샘플이 벽면에 달라붙는 것을 방지하여 분무건조 중 샘플 손실을 줄일 수 있습니다.
- 메서드를 저장하고 다음 분석 때 이를 활용하여 여러분의 분석 효율성을 높이세요. 또한, 편의성을 높이기 위해 Mini Spray Dryer S-300 (소형 분무 건조기)에서 샘플을 순차적으로 처리하도록 샘플 대기 리스트를 프로그래밍할 수도 있습니다.
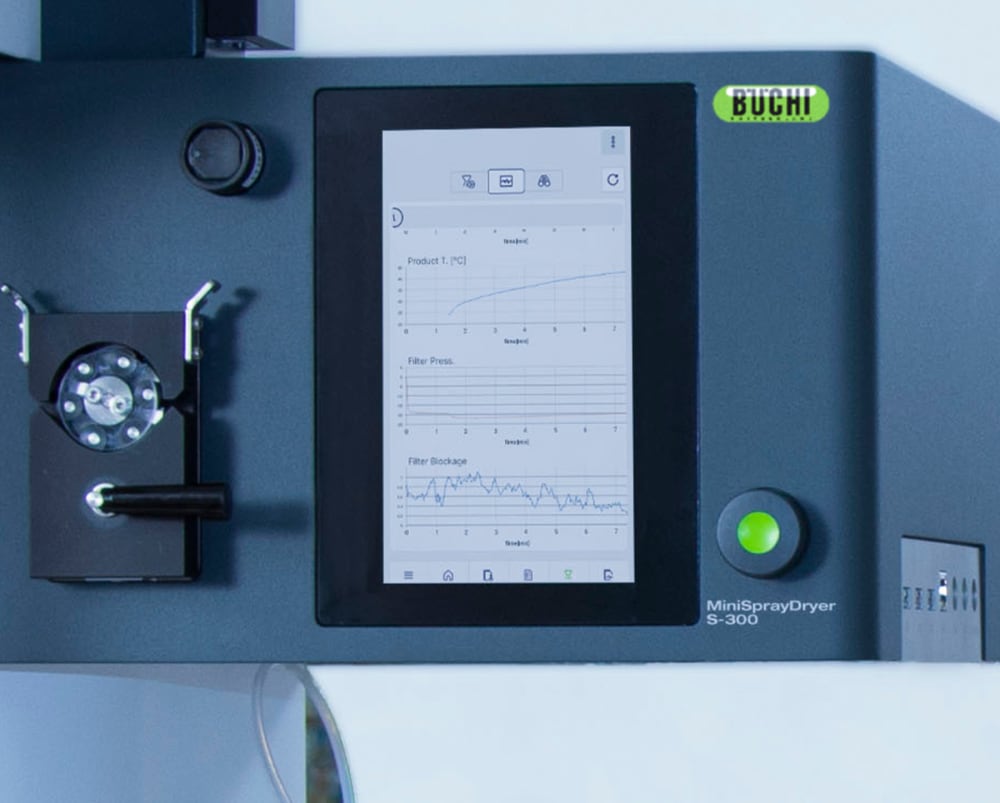
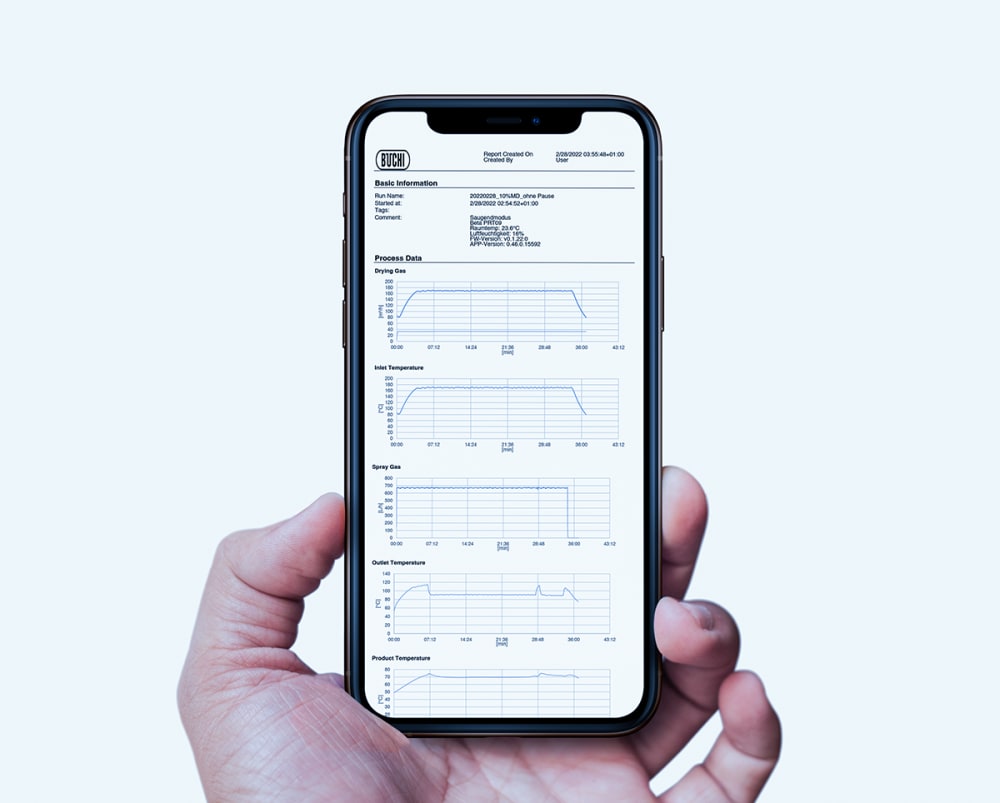
- Mini Spray Dryer S-300 (소형 분무 건조기)에서 수행하는 모든 실행은 장비에 기록 및 저장됩니다. 버튼을 누르면 공정 프로세스 데이터에 대한 PDF 파일 또는 .csv 파일을 쉽게 생성할 수 있습니다.
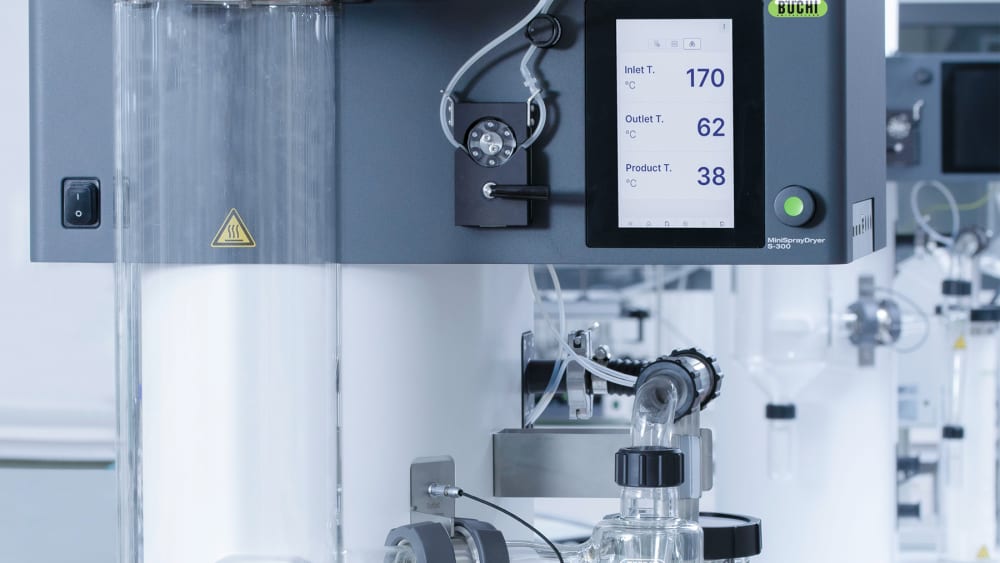
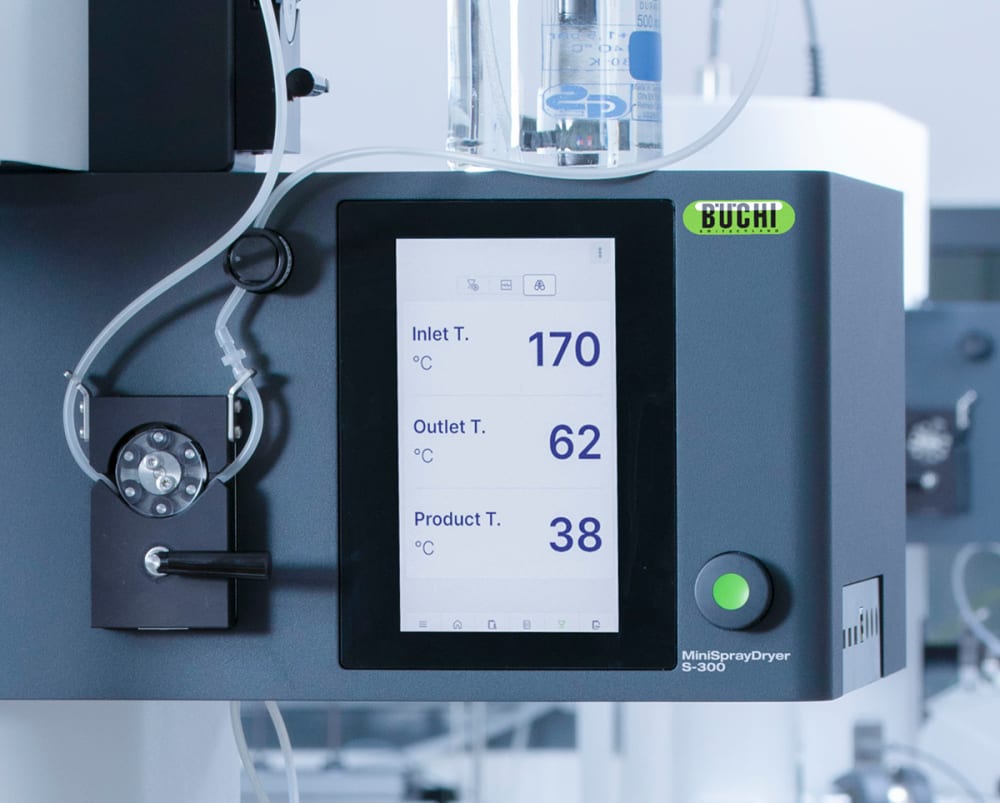
- 열이 샘플에 미치는 영향에 대한 자세한 정보를 제공하기 위해 Mini Spray Dryer S-300 (소형 분무 건조기)은 사용자가 배출구(outlet)와 최종 생산물의 온도를 모두 모니터링할 수 있습니다. 특히, 이 정보는 열에 민감한 샘플을 분무건조할 때 샘플을 보호할 수 있도록 도와줍니다.
- 분무 기체, 건조 기체 및 펌프 속도와 같은 Mini Spray Dryer S-300 (소형 분무 건조기)의 모든 파라미터는 SI 값으로 제공되며 시스템에서 자동으로 조절됩니다. 이러한 기능은 공정의 재현성을 극대화합니다.
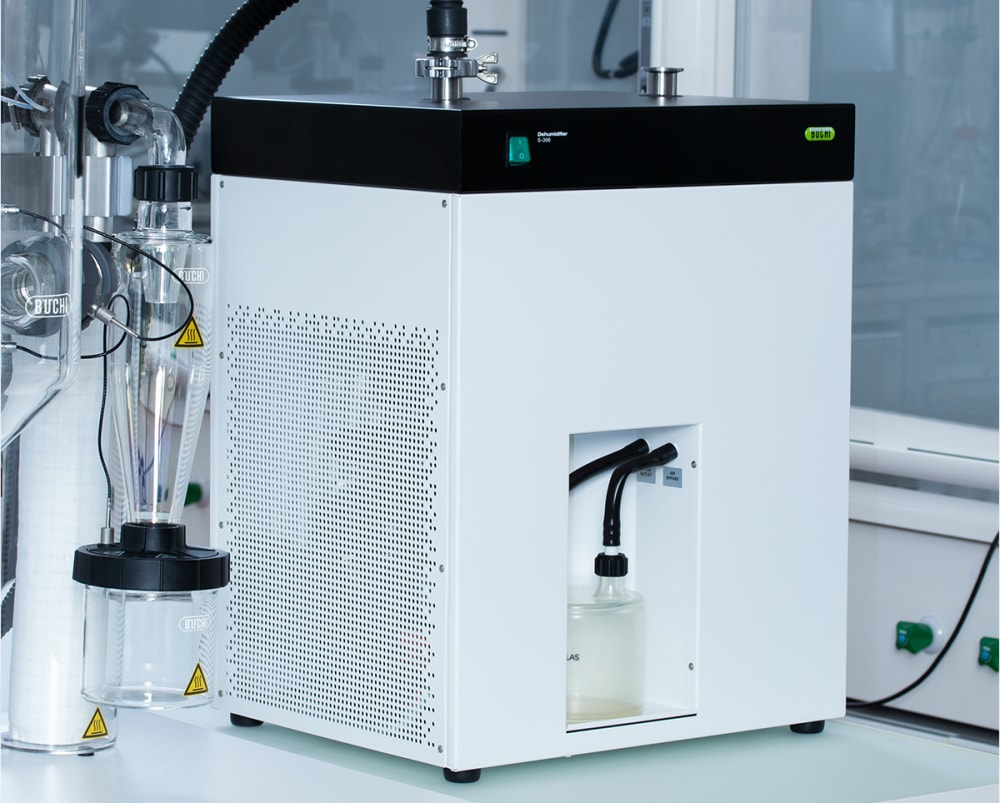
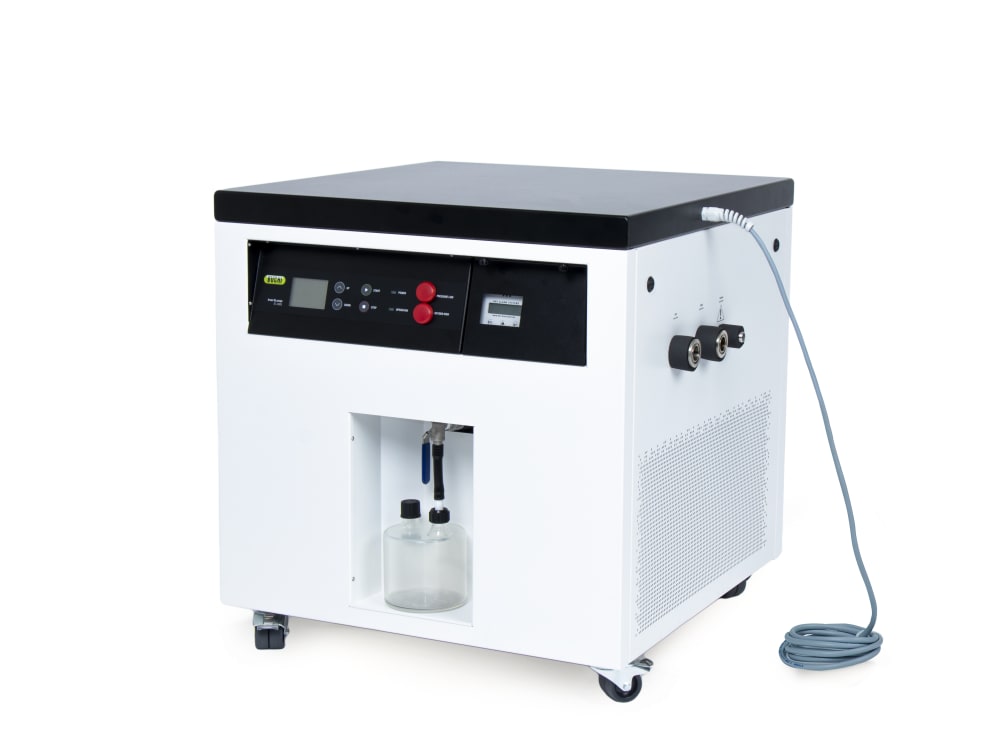
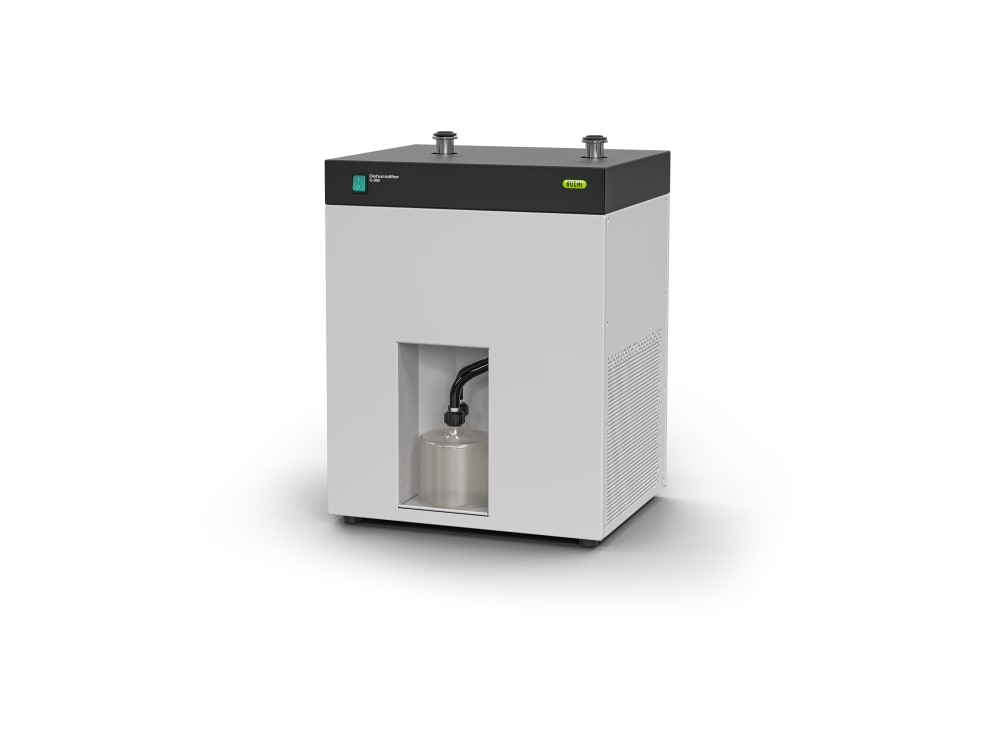
- Inert Loop S-395 (불활성 루프)와 Mini Spray Dryer S-300 (소형 분무 건조기)의 조합은 유기용매 샘플을 안전하게 취급할 수 있도록 합니다. 질소 건조 기체는 순환되며 용매는 응축되어 수집됩니다. 안전을 위해 시스템 내 산소 레벨과 기체 흐름은 지속적으로 모니터링됩니다.
Compare the Mini Spray Dryer S-300 (소형 분무 건조기)
관련 부품 및 액세서리
다운로드
- Technical Data Sheet Mini Spray Dryer S-300(pdf)
- Product Brochure Mini Spray Dryer S-300 en(pdf)
- Product Brochure Pharma and Chemistry en(pdf)
- Operation Manual Mini Spray Dryer S-300 en(pdf)
- Installation Manual Mini Spray Dryer S-300 in closed mode with Inert Loop(pdf)
- Installation Manual Mini Spray Dryer S-300 in closed mode with Dehumidifier and Inert Loop(pdf)
- Installation Manual Mini Spray Dryer S-300 in open suction mode(pdf)
- Installation Manual Mini Spray Dryer S-300 in open pressure mode(pdf)
- Configuration guide S-300(pdf)
- Pre-Installation Checklist Mini Spray Dryer S-300(pdf)
관련 기기
관련 과정 및 교육
응용자료
모든 범위의 응용 분야를 위한 탁월한 유연성
Batteries
Laboratory-scale spray drying is a valuable technique in battery research for the fabrication of electrode materials. It enables precise control over particle size and morphology, resulting in electrodes with optimized electrochemical performance. Spray drying allows for the production of fine and uniform particles, contributing to the development of high-performance batteries. This method facilitates the development of electrode materials with enhanced properties, such as improved conductivity and electrochemical stability. By employing laboratory-scale spray drying in battery research, scientists can advance energy storage technologies and develop more efficient and reliable batteries for various applications.
Biotech
Applications: Cells, bacteria and protein encapsulation, cell transplantation, biotransformation Methods: Drying, encapsulation of liquids, Encapsulation of solids, Micronization, Cell encapsulation Instruments used: Mini Spray Dryer S-300, Nano Spray Dryer B-90, Encapsulator B-390 / B-395, Lyovapor L-200 / L-300
Chemicals / Materials
Laboratory-scale spray drying is a versatile and efficient method for producing a wide range of materials in the chemicals and materials science field. In recent years, notable trends have emerged, including the application of spray drying for nano materials, paints and coatings, and catalysts. One trend is the use of laboratory-scale spray drying in the synthesis of nano materials. This technique enables the production of nanoparticles and nanostructured materials with controlled size, morphology, and composition. By tailoring these properties, researchers can develop advanced materials with improved mechanical strength, enhanced conductivity, and tailored surface functionalities. Spray drying also finds application in the production of paints and coatings. By producing fine and uniform particles, spray drying contributes to the desired properties of coatings, such as improved color, durability, and film formation. This trend leads to the development of high-quality coatings with enhanced performance and functionality. Furthermore, laboratory-scale spray drying plays a role in the development of catalysts. By controlling particle size, composition, and surface area, spray drying allows for the design and optimization of catalysts for efficient chemical transformations and environmental applications. In summary, laboratory-scale spray drying in the chemicals and materials science field is witnessing trends in nano materials, paints and coatings, and catalysts. These trends contribute to the development of advanced materials, high-performance coatings, and efficient catalysts, driving innovation in various industries.
Cosmetics
Applications: Cosmetics, fragrances Methods: Drying, encapsulation of liquids, Encapsulation of solids, Micronization Instruments used: Mini Spray Dryer S-300, Encapsulator B-390 / B-395, Lyovapor L-200 / L-300
Food
Applications: Encapsulation of additives, controlled release, nutraceuticals, functional foods, flavors, vitamins, proteins, probiotic bacteria, juice concentrate, milk powder Methods: Drying, encapsulation of liquids, Encapsulation of solids, Micronization Instruments used: Mini Spray Dryer S-300, Encapsulator B-390 / B-395, Lyovapor L-200 / L-300
Pharma
Laboratory-scale spray drying is a vital process in the pharmaceutical industry, used for the formulation and development of various drugs and medications. It involves converting liquid solutions or suspensions into dry powders through atomization and rapid evaporation. This technique offers several benefits, including improved stability, enhanced bioavailability, and ease of handling. In recent years, several notable trends have emerged in laboratory-scale spray drying within the pharmaceutical sector. One significant trend is the use of spray drying for the production of solid dispersions. Solid dispersions are formulations where the drug is dispersed in a solid matrix, enhancing its solubility and dissolution rate. Spray drying enables the preparation of solid dispersion powders with uniform drug distribution, leading to improved drug delivery and efficacy. Another trend is the development of inhalable drugs using spray drying. This technique allows for the production of dry powder formulations suitable for inhalation, facilitating targeted delivery to the respiratory system. Inhalable drugs offer advantages in the treatment of respiratory diseases, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Taste masking is another important application of laboratory-scale spray drying. By encapsulating drugs with unpleasant taste profiles in taste-masking particles, the palatability of oral formulations can be improved. Spray drying enables the encapsulation of drugs within taste-masking coatings, leading to better patient compliance, particularly for pediatric and geriatric populations. Furthermore, laboratory-scale spray drying is increasingly employed for the development of controlled-release formulations. By incorporating drugs into sustained-release matrices or encapsulating them within microspheres or nanoparticles, spray drying allows for the controlled release of drugs over an extended period. This enables optimized drug dosage regimens and improved patient convenience. In conclusion, laboratory-scale spray drying in the pharmaceutical area is witnessing several significant trends, including the production of solid dispersions, inhalable drugs, taste-masking formulations, and controlled-release systems. These trends contribute to the development of novel drug formulations with enhanced solubility, targeted delivery, improved patient compliance, and optimized drug release profiles.