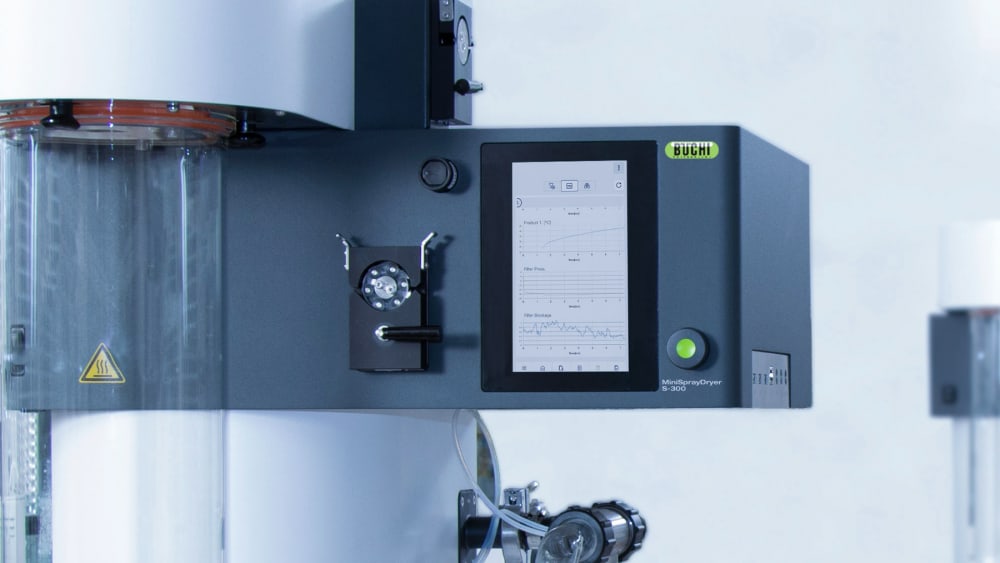
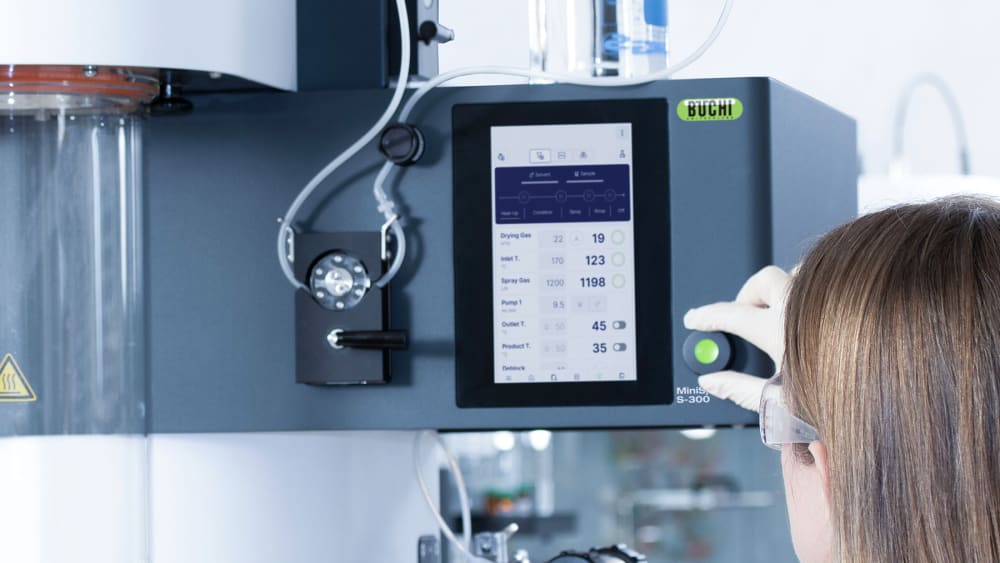
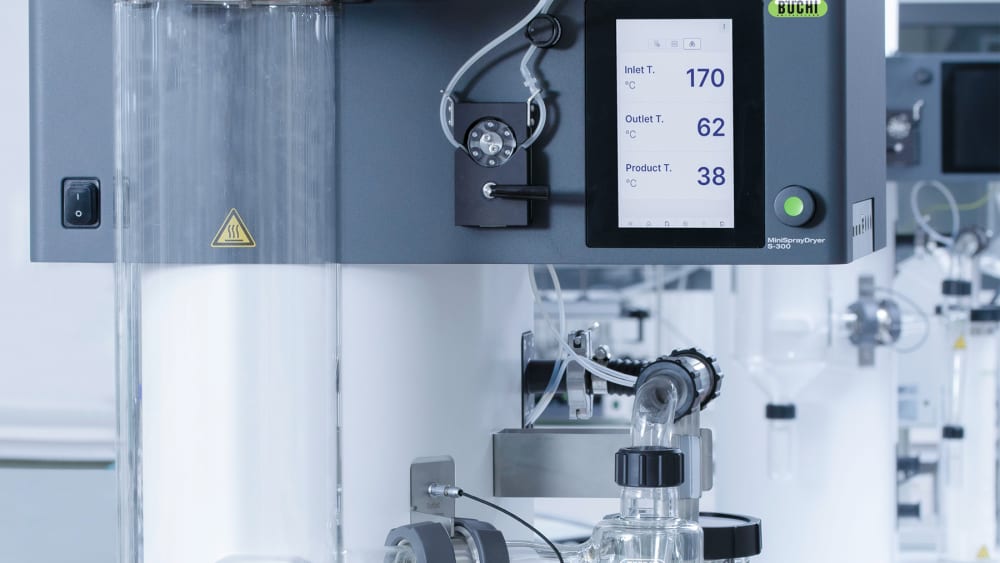
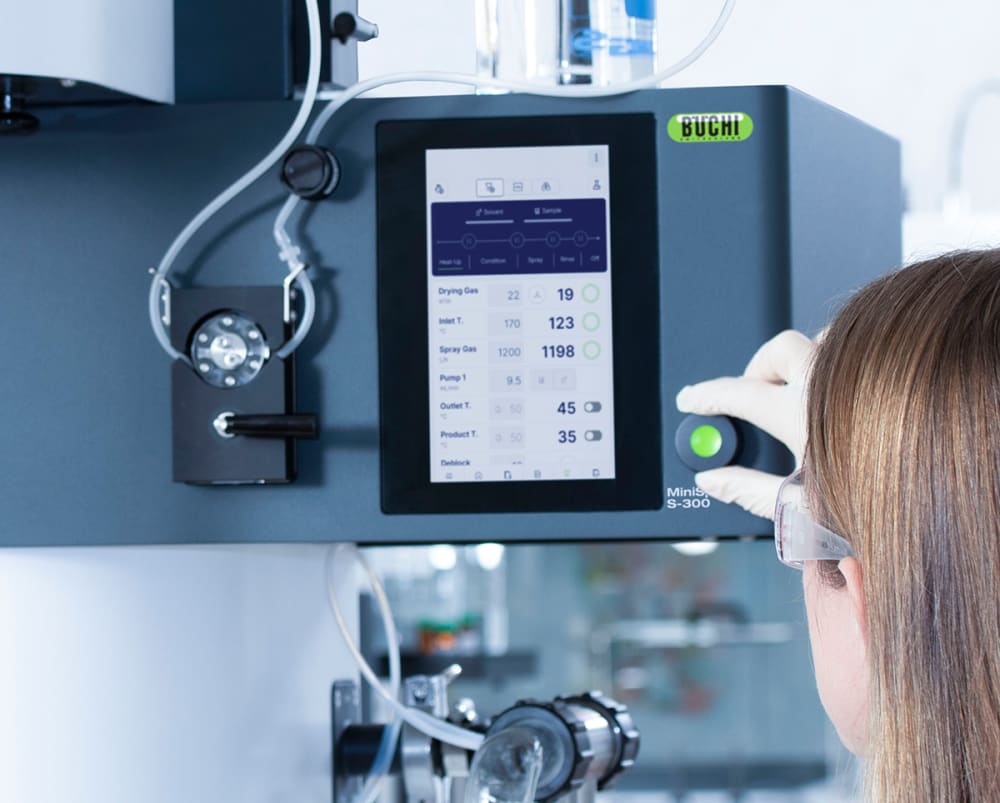
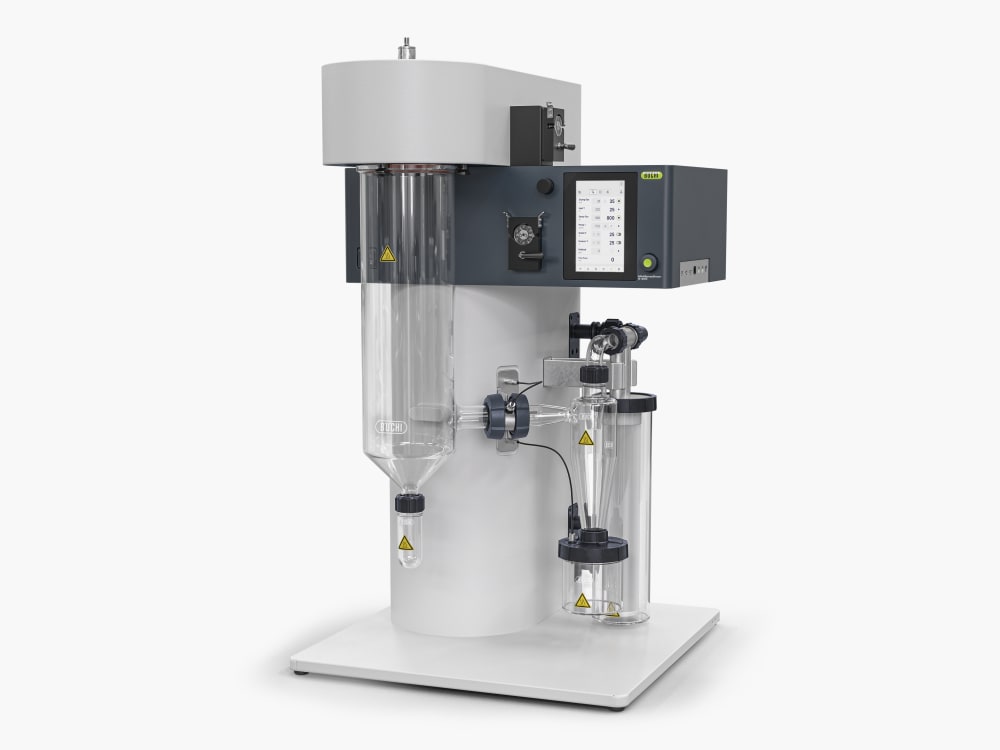
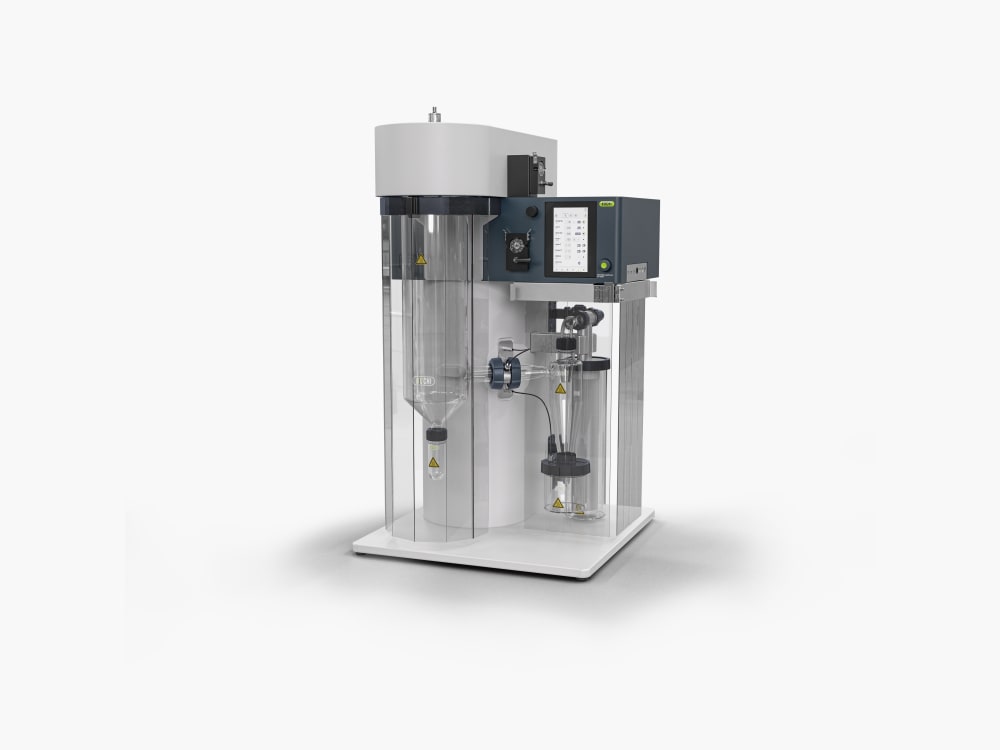
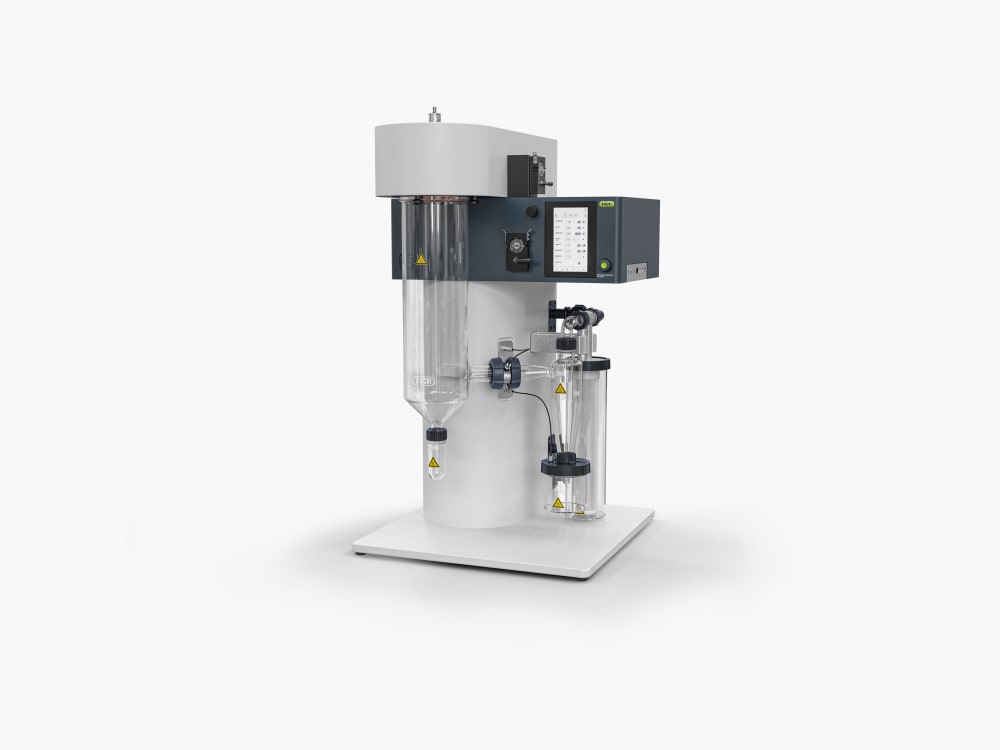
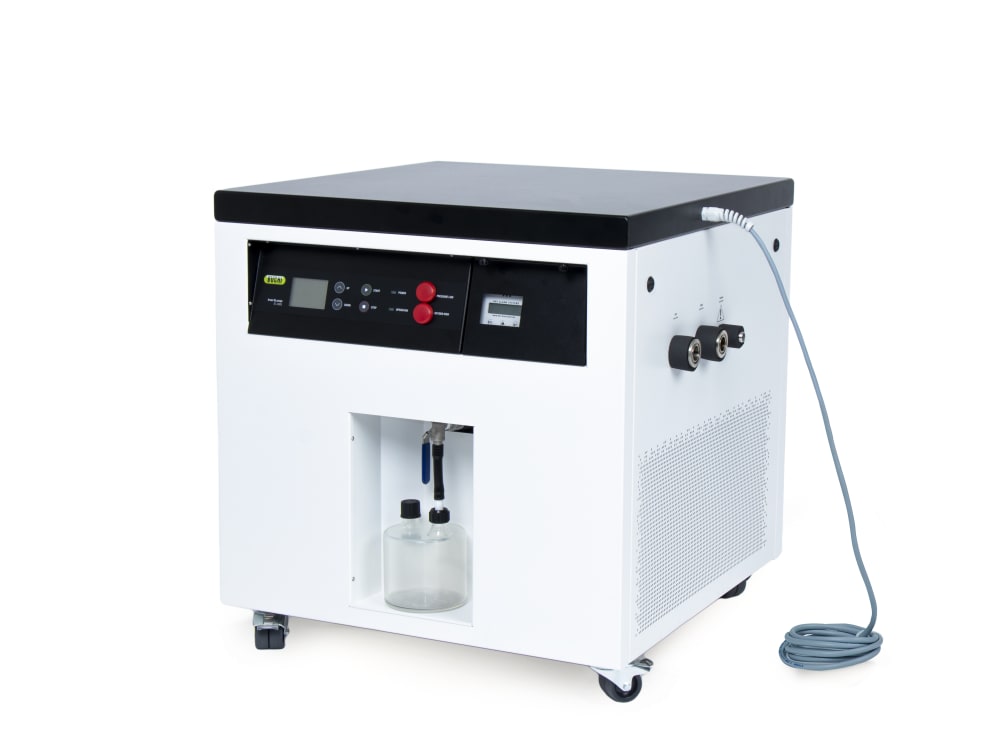
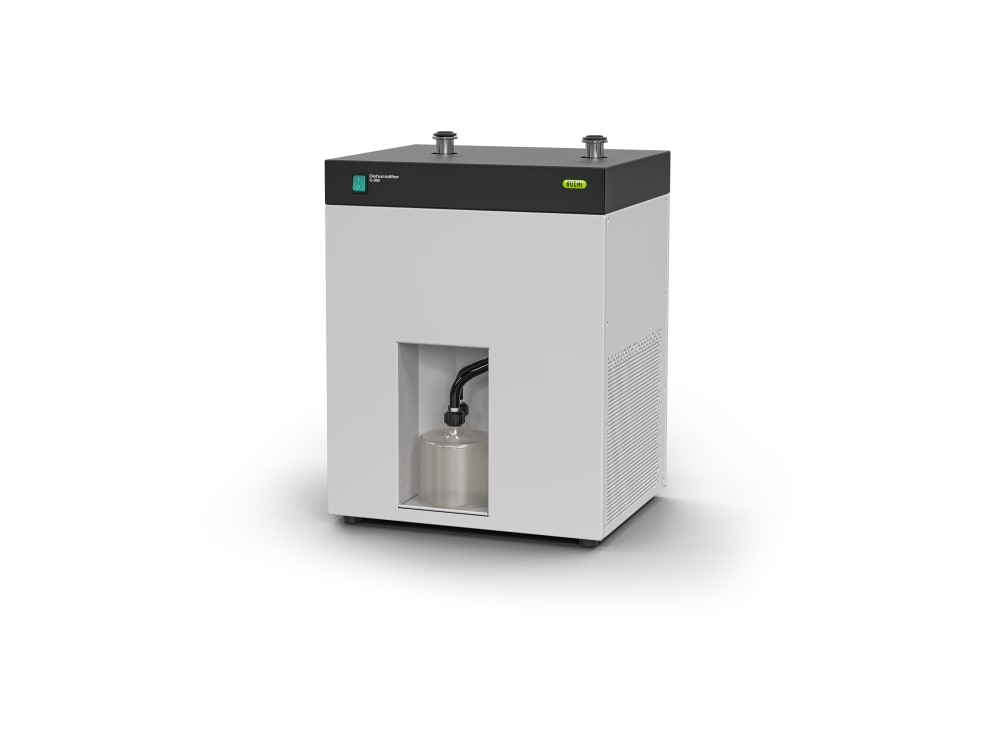
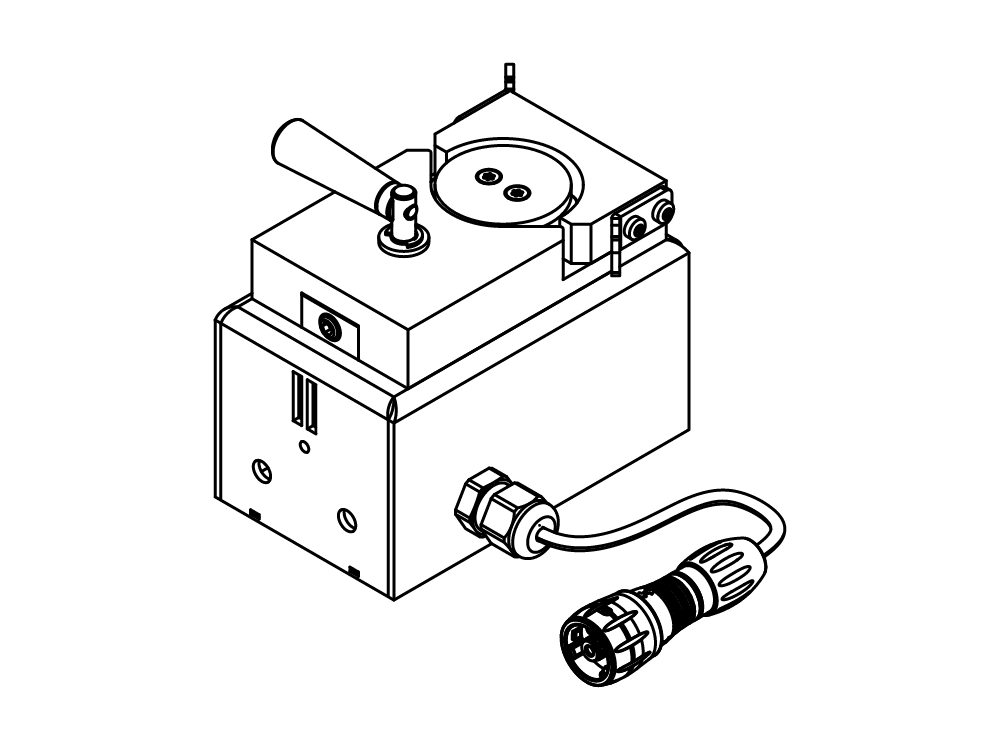
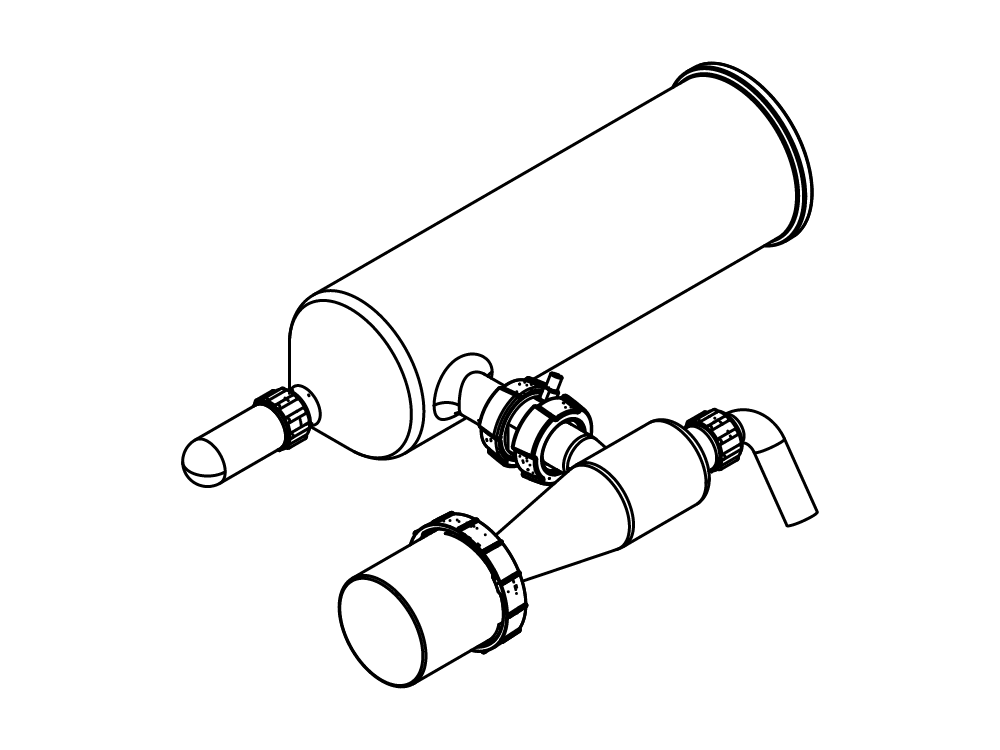
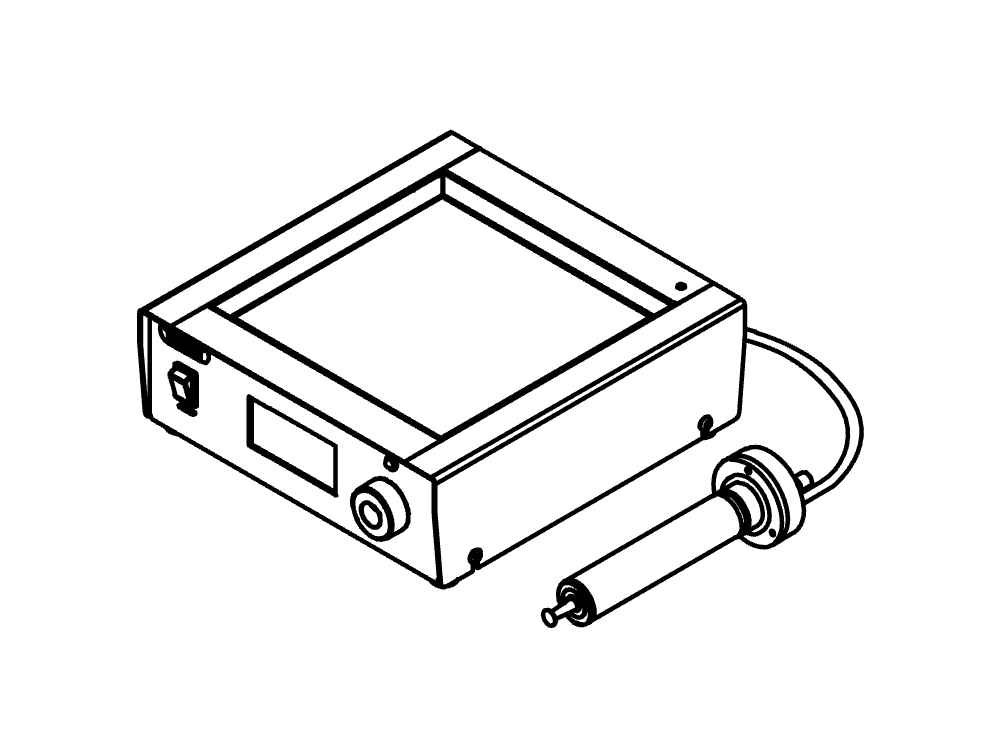
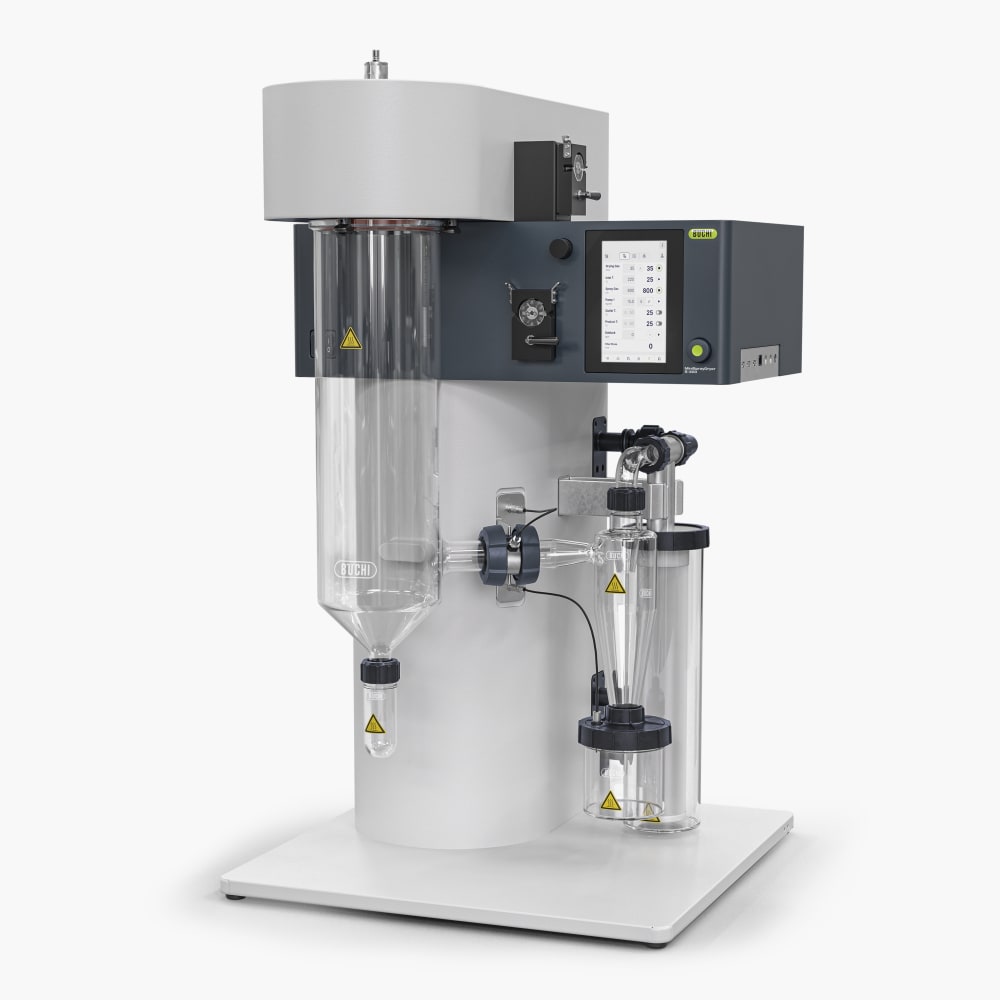
Mini atomiseur S-300
L’atomiseur de laboratoire de nouvelle génération
Avec le Mini atomiseur S-300, BUCHI consolide sa position de leader mondial du marché depuis plus de 40 ans. Cet instrument de laboratoire associe une conception exceptionnelle à des capacités uniques pour offrir une expérience utilisateur extraordinaire.

Caractéristiques
- Commandez ou surveillez le Mini atomiseur S-300 sans limite de lieu ni de temps. Installez l’application sur n’importe quel ordinateur ou appareil mobile pour disposer d’un accès complet à l’interface utilisateur de l’atomiseur de laboratoire. Grâce aux options de commande à distance, vous gérez votre temps avec davantage de souplesse et réagissez rapidement en cas de fluctuation du process.
- Avec plus de 40 ans d’expérience dans le séchage par pulvérisation à l’échelle du laboratoire, BUCHI a accumulé un immense savoir-faire de nombreuses applications. Recherchez parmi les milliers de publications des bibliothèques scientifiques le document de votre choix sur les atomiseurs BUCHI ou explorez notre base de données en ligne des applications de séchage par pulvérisation pour trouver celles qui répondront à vos besoins. Grâce au Mini atomiseur S-300, vous pouvez reproduire les résultats obtenus avec les anciens modèles d’atomiseurs de laboratoire BUCHI. Vous ne perdrez rien de vos précieux travaux, et le transfert vers le nouvel instrument est à la fois très rapide et très simple.
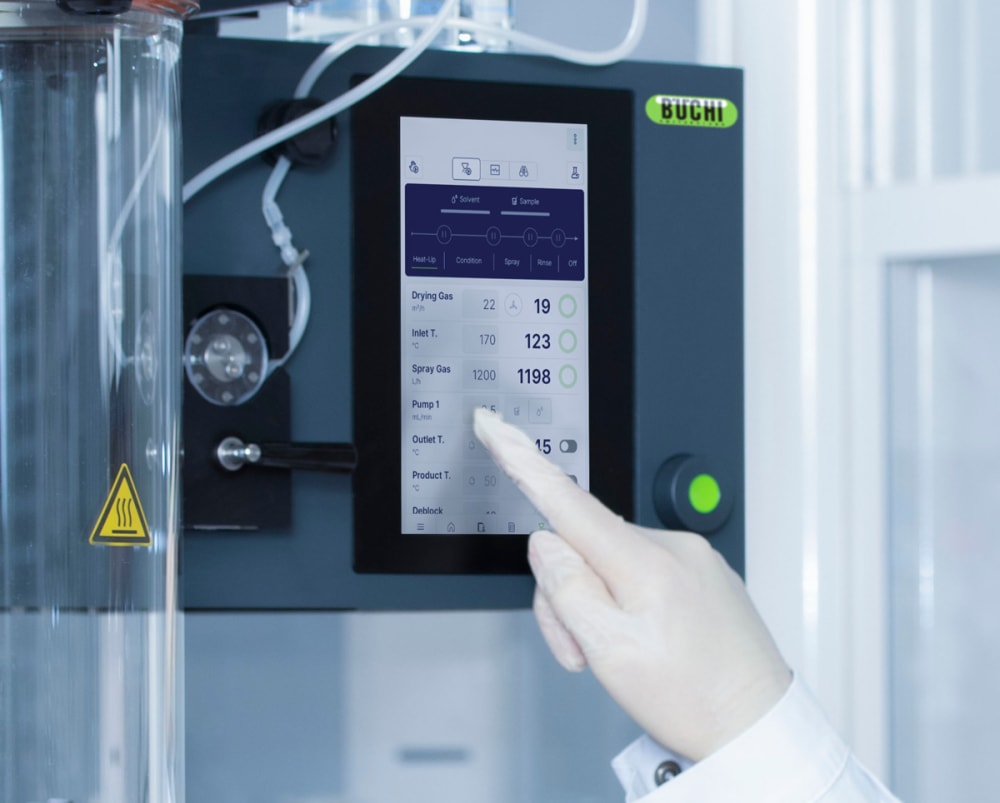
- Le mode automatique permet de programmer votre Mini atomiseur S-300 avancé et d’exécuter automatiquement votre méthode. L’atomiseur de laboratoire chauffe, commande la température de sortie, pulvérise du solvant pur, puis votre échantillon, puis à nouveau du solvant pur et s’arrête après le traitement de l’échantillon. Le mode auto accélère efficacement votre process, surtout lors des tâches répétitives.
- Réduisez les pertes d’échantillon lors du séchage par pulvérisation en laboratoire grâce à un cyclone doté d’un revêtement conducteur qui limite l’adhérence aux parois.
- Gagnez en rapidité et en sérénité en enregistrant les cycles en tant que méthodes et en les répétant ultérieurement. Pour plus de commodité, vous pouvez également programmer une file d’échantillons qui seront traités l’un après l’autre sur votre Mini atomiseur S-300.
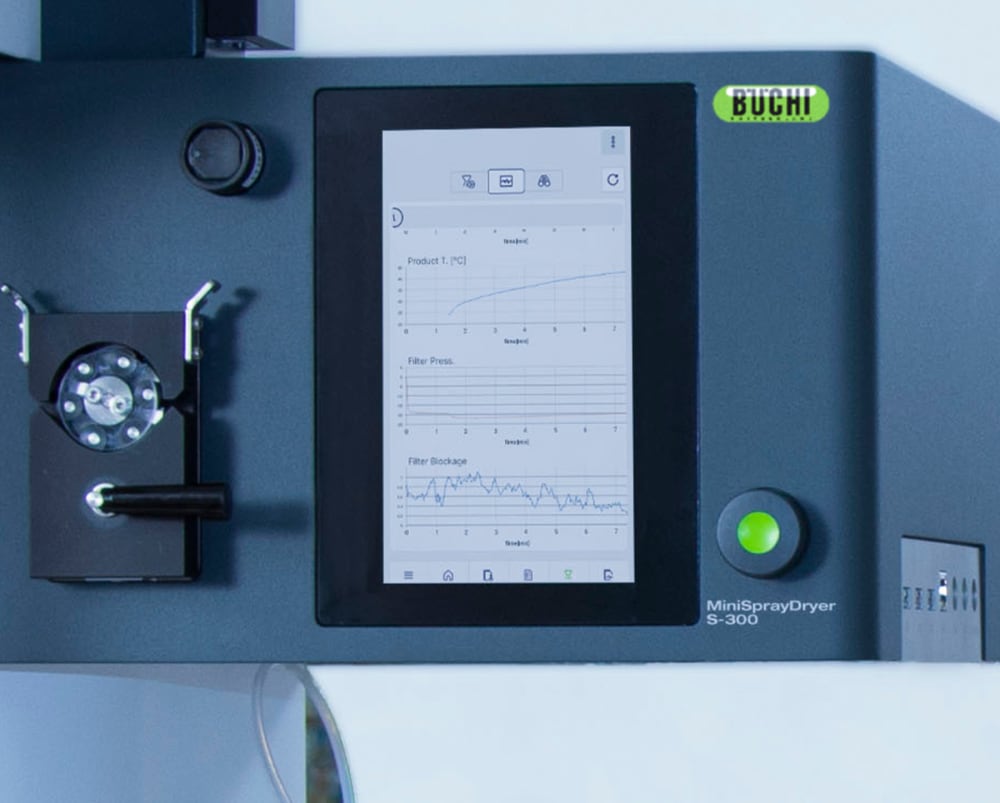
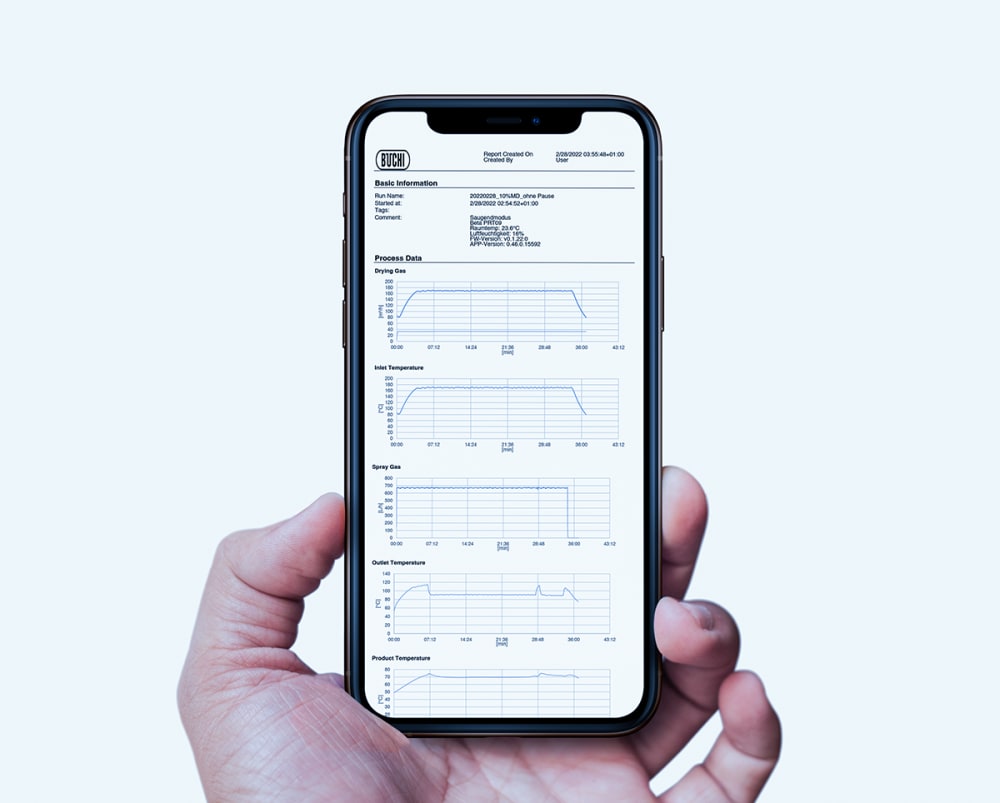
- Tous les cycles effectués sur le Mini atomiseur S-300 sont consignés et sauvegardés sur l’instrument. D’un simple appui sur un bouton, vous pouvez aisément générer un rapport PDF ou un fichier .csv contenant vos données de process.
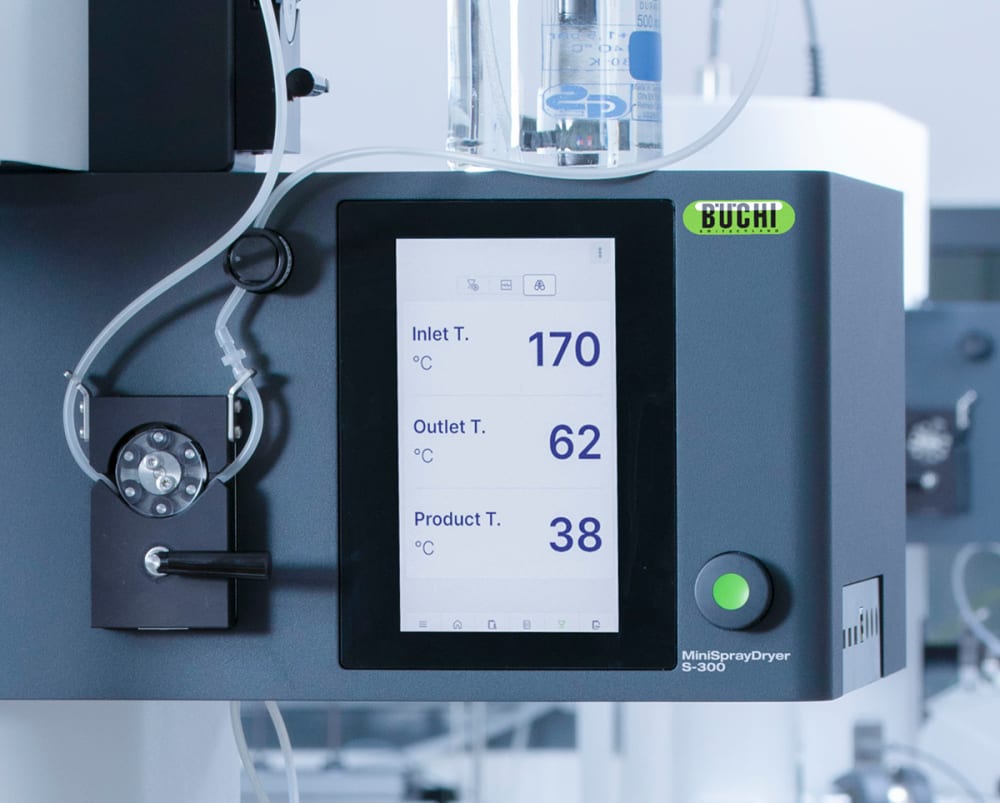
- Afin de mieux connaître les influences thermiques subies par votre échantillon, le Mini atomiseur S-300 permet de surveiller la température de sortie et celle du produit final. Ces données peuvent vous aider à mieux protéger vos échantillons, notamment lorsqu’ils sont thermosensibles et séchés par pulvérisation.
- Tous les paramètres du Mini atomiseur S-300, comme les gaz de pulvérisation et de séchage ainsi que la vitesse de la pompe, sont exprimés en valeurs SI et automatiquement régulés par le système. Ces fonctionnalités optimisent la reproductibilité de votre process.
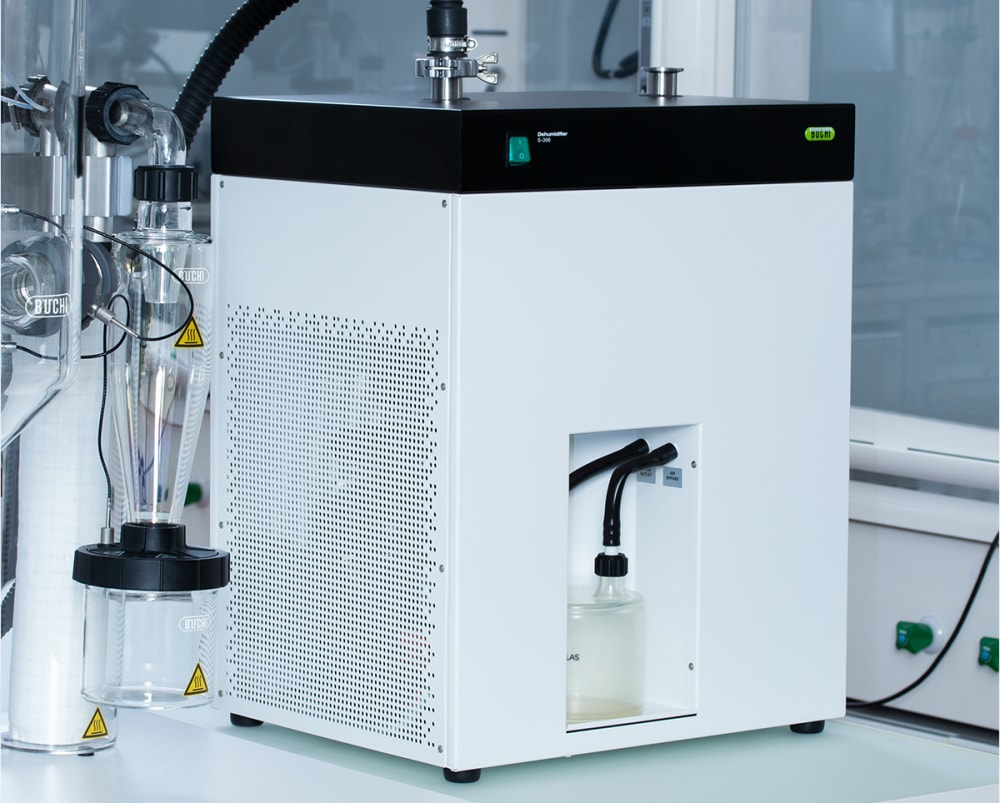
- Lorsqu’il est associé à l’Inert Loop S-395, le Mini atomiseur S-300 permet de manipuler en toute sécurité les échantillons contenant des solvants organiques. L’azote gazeux utilisé pour le séchage est mis en circulation et le solvant est recueilli sous forme de condensat. Pour votre sécurité, le taux d’oxygène et le débit de gaz sont contrôlés en permanence dans le système.
Compare the Mini atomiseur S-300
Pièces & Accessoires correspondants
Téléchargements
- Technical Data Sheet Mini Spray Dryer S-300(pdf)
- Product Brochure Mini Spray Dryer S-300 en(pdf)
- Product Brochure Pharma and Chemistry en(pdf)
- Operation Manual Mini Spray Dryer S-300 en(pdf)
- Installation Manual Mini Spray Dryer S-300 in closed mode with Inert Loop(pdf)
- Installation Manual Mini Spray Dryer S-300 in closed mode with Dehumidifier and Inert Loop(pdf)
- Installation Manual Mini Spray Dryer S-300 in open suction mode(pdf)
- Installation Manual Mini Spray Dryer S-300 in open pressure mode(pdf)
- Configuration guide S-300(pdf)
- Pre-Installation Checklist Mini Spray Dryer S-300(pdf)
Instruments correspondants
Cours & Formations correspondants
Applications
Unmatched flexibility for a full range of applications
Batteries
Laboratory-scale spray drying is a valuable technique in battery research for the fabrication of electrode materials. It enables precise control over particle size and morphology, resulting in electrodes with optimized electrochemical performance. Spray drying allows for the production of fine and uniform particles, contributing to the development of high-performance batteries. This method facilitates the development of electrode materials with enhanced properties, such as improved conductivity and electrochemical stability. By employing laboratory-scale spray drying in battery research, scientists can advance energy storage technologies and develop more efficient and reliable batteries for various applications.
Biotech
Applications: Cells, bacteria and protein encapsulation, cell transplantation, biotransformation Methods: Drying, encapsulation of liquids, Encapsulation of solids, Micronization, Cell encapsulation Instruments used: Mini Spray Dryer S-300, Nano Spray Dryer B-90, Encapsulator B-390 / B-395, Lyovapor L-200 / L-300
Chemicals / Materials
Laboratory-scale spray drying is a versatile and efficient method for producing a wide range of materials in the chemicals and materials science field. In recent years, notable trends have emerged, including the application of spray drying for nano materials, paints and coatings, and catalysts. One trend is the use of laboratory-scale spray drying in the synthesis of nano materials. This technique enables the production of nanoparticles and nanostructured materials with controlled size, morphology, and composition. By tailoring these properties, researchers can develop advanced materials with improved mechanical strength, enhanced conductivity, and tailored surface functionalities. Spray drying also finds application in the production of paints and coatings. By producing fine and uniform particles, spray drying contributes to the desired properties of coatings, such as improved color, durability, and film formation. This trend leads to the development of high-quality coatings with enhanced performance and functionality. Furthermore, laboratory-scale spray drying plays a role in the development of catalysts. By controlling particle size, composition, and surface area, spray drying allows for the design and optimization of catalysts for efficient chemical transformations and environmental applications. In summary, laboratory-scale spray drying in the chemicals and materials science field is witnessing trends in nano materials, paints and coatings, and catalysts. These trends contribute to the development of advanced materials, high-performance coatings, and efficient catalysts, driving innovation in various industries.
Cosmetics
Applications: Cosmetics, fragrances Methods: Drying, encapsulation of liquids, Encapsulation of solids, Micronization Instruments used: Mini Spray Dryer S-300, Encapsulator B-390 / B-395, Lyovapor L-200 / L-300
Food
Applications: Encapsulation of additives, controlled release, nutraceuticals, functional foods, flavors, vitamins, proteins, probiotic bacteria, juice concentrate, milk powder Methods: Drying, encapsulation of liquids, Encapsulation of solids, Micronization Instruments used: Mini Spray Dryer S-300, Encapsulator B-390 / B-395, Lyovapor L-200 / L-300
Pharma
Laboratory-scale spray drying is a vital process in the pharmaceutical industry, used for the formulation and development of various drugs and medications. It involves converting liquid solutions or suspensions into dry powders through atomization and rapid evaporation. This technique offers several benefits, including improved stability, enhanced bioavailability, and ease of handling. In recent years, several notable trends have emerged in laboratory-scale spray drying within the pharmaceutical sector. One significant trend is the use of spray drying for the production of solid dispersions. Solid dispersions are formulations where the drug is dispersed in a solid matrix, enhancing its solubility and dissolution rate. Spray drying enables the preparation of solid dispersion powders with uniform drug distribution, leading to improved drug delivery and efficacy. Another trend is the development of inhalable drugs using spray drying. This technique allows for the production of dry powder formulations suitable for inhalation, facilitating targeted delivery to the respiratory system. Inhalable drugs offer advantages in the treatment of respiratory diseases, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Taste masking is another important application of laboratory-scale spray drying. By encapsulating drugs with unpleasant taste profiles in taste-masking particles, the palatability of oral formulations can be improved. Spray drying enables the encapsulation of drugs within taste-masking coatings, leading to better patient compliance, particularly for pediatric and geriatric populations. Furthermore, laboratory-scale spray drying is increasingly employed for the development of controlled-release formulations. By incorporating drugs into sustained-release matrices or encapsulating them within microspheres or nanoparticles, spray drying allows for the controlled release of drugs over an extended period. This enables optimized drug dosage regimens and improved patient convenience. In conclusion, laboratory-scale spray drying in the pharmaceutical area is witnessing several significant trends, including the production of solid dispersions, inhalable drugs, taste-masking formulations, and controlled-release systems. These trends contribute to the development of novel drug formulations with enhanced solubility, targeted delivery, improved patient compliance, and optimized drug release profiles.